给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
- 标签:
两层 for 循环
- 利用两层 for 循环,遍历每一个元素,再将差值与其后元素一一比对,也称为「暴力法」,如果两个目标值在最后,效率很低
- 时间复杂度为:O(n^2):n + (n-1) + .... + 1
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
// Java
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] == target - nums[i]) {
return new int[]{i, j}; // 返回数组最简洁的方式
}
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution"); // 非法参数异常:整数数组和目标值不符合条件
}
}// JavaScript
var twoSum = function (nums, target) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] === target - nums[i]) {
return [i, j];
}
}
}
};// Go
func twoSum1(nums []int, target int) []int {
var n = len(nums)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
var x = nums[i]
// 线性查找
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
if nums[j] == target - x {
return []int{i, j}
}
}
}
return []int{}
}class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]// Java
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// s = [5, 0, 2]; 0 1 2
// s2 = [0, 2, 5] 2 0 1
Arrays.sort(nums);
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[]{nums[left], nums[right]};
}
else if (sum > target) right--;
else left++;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution"); // 非法参数异常:整数数组和目标值不符合条件
}
}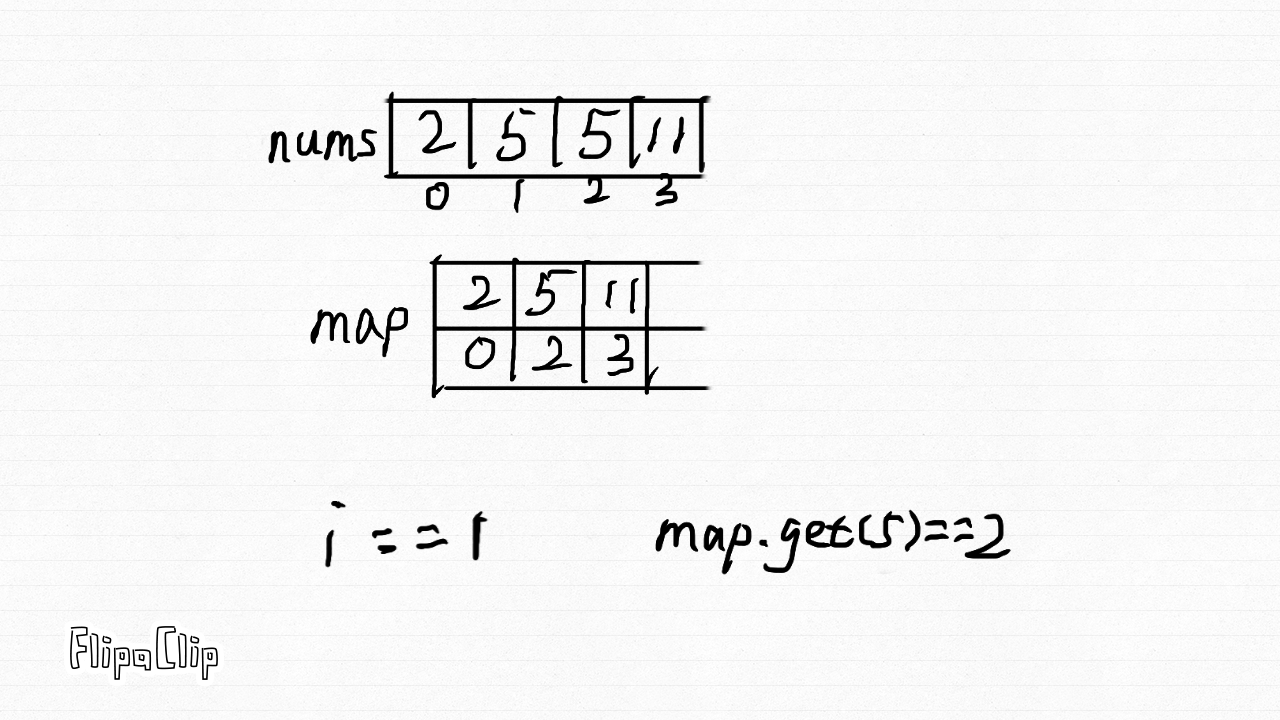
- 标签:
哈希表
- 「暴力法」时间复杂度高,因为差值要一一和其后元素比较,如果差值一次就能和其他所有元素比较,那么时间复杂度为 O(n)
- 可以利用哈希表的 contains() 实现此功能
- 因为需要返回索引,所以元素和索引要相关联,所以使用 Map 结构
- 因为要返回索引,假设索引作为 key,元素作为 value,不能根据 value(元素)反推其 key(索引),所以元素作为 key,索引作为 value
- 虽然数组中元素可重复,重复元素作为 key 加入 map 时,value(索引)更新,此时索引代表重复元素。所以重复元素无影响
- 两遍哈希表,第一遍将数据存放到 map 中,第二遍使用 contains() 方法
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
// Java
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 引用对象使用 <Integer, Integer> 可指定存储类型
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i); // 元素作为 key,索引作为 value
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int key = target - nums[i];
// map.containsKey(key) 相当于 map.keySet().contains(key);
// 利用 && 特性:如果 map.containsKey(key) 为 false,map.get(key) 将不执行,避免空指针异常;
// map.get(key) != i: 索引不同,确保不是同一个元素
if (map.containsKey(key) && map.get(key) != i) {
return new int[]{i, map.get(key)};
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
}// JavaScript
var twoSum = function (nums, target) {
var map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.set(nums[i], i);
}
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
let key = target - nums[i];
if (map.has(key) && map.get(key) !== i) {
return [i, map.get(key)];
}
}
};class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
num_dict = {nums[index]: index for index in range(len(nums))}
for index in range(len(nums)):
other_index = num_dict.get((target - nums[index]), -1)
if other_index != -1 and other_index != index:
return [index, other_index]
- 标签:
哈希表
- 可将第一遍哈希省略,每次循环,将元素、索引存于 map,当前元素可与 map 中已加入的元素比较
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
// Java
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int key = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(key)) { // 跟 map 中已加入元素比较,肯定不是同一个元素,所以不比较索引
return new int[]{map.get(key), i}; // i 在后
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
}// JavaScript
var twoSum = function (nums, target) {
var map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
let key = target - nums[i];
if (map.has(key) && map.get(key) !== i) {
return [map.get(key), i];
}
map.set(nums[i], i);
}
};class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
num_dict = {}
for index in range(len(nums)):
other_num = target - nums[index]
if other_num in num_dict.keys():
return [num_dict[other_num], index]
num_dict[nums[index]]=index
| 描述 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| nums |
[2, 7, 11, 15] |
[3, 2, 4] |
[3, 3] |
[2, 5, 5, 11] |
| target |
9 |
6 |
6 |
10 |
| 预期结果 |
[0, 1] |
[1, 2] |
[0, 1] |
[1, 2] |
