[toc]
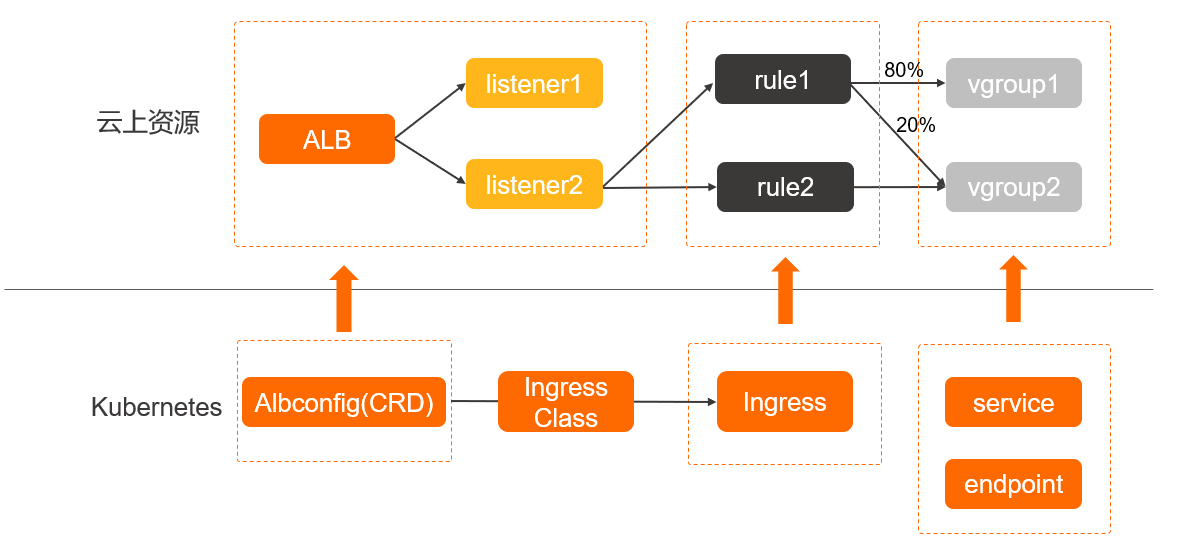
In a Kubernetes cluster, an Ingress functions as an access point that exposes Services in the cluster. It distributes most of the network traffic that is destined for the Services in the cluster. An Ingress is a Kubernetes resource. It manages external access to the Services in a Kubernetes cluster. You can configure forwarding rules for an Ingress to route network traffic to backend pods of different Services.
The ALB Ingress controller retrieves the changes to Ingresses from the API server and dynamically generates AlbConfig objects when Ingresses changes are detected. Then, the ALB Ingress controller performs the following operations in sequence: create ALB instances, configure listeners, create Ingress rules, and configure backend server groups. The Services, the Ingresses, and the AlbConfig objects interact with each other in the following ways:
- A Service is an abstraction of an application that is deployed in a group of replicated pods.
- An Ingress contains reverse proxy rules. It controls to which Services HTTP or HTTPS requests are routed. For example, an Ingress routes requests to different Services based on the hosts and URLs in the requests.
- An AlbConfig object is a CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) object that the ALB Ingress controller uses to configure ALB instances and listeners. An AlbConfig object corresponds to one ALB instance.
Note: ALB instances that serve Ingresses are fully managed by the ALB Ingress controller. To avoid service interruptions caused by Ingress errors, we recommend that you do not modify these ALB instances in the ALB console. For more information about the quotas related to ALB, see Limits.
ALB Ingresses are compatible with NGINX Ingresses and provide improved traffic management based on ALB instances. ALB Ingresses support complex routing, automatic certificate discovery, and the HTTP, HTTPS, and Quick UDP Internet Connection (QUIC) protocols. These features fully meet the requirements of cloud-native applications for ultra-high elasticity and balancing of heavy traffic loads at Layer 7.
Prerequisites
-
A Kubernetes cluster is created and Load Balancer Controller is installed. For more information, see Installation.
-
kubectl is used to connect to the cluster and operations such as get and apply can be performed on the cluster.
-
An ALB instance is created by using AlbConfig. For more information, see Installation.
-
A basic deployment set and a Service are created. Example:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: demo-service namespace: default spec: ports: - name: port1 port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 selector: app: demo sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: demo namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: demo template: metadata: labels: app: demo spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/alb-sample/cafe:v1 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: demo ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP
Perform the following steps to create an Ingress with a domain name and an Ingress without a domain name, and then use the Ingresses to forward requests.
-
Create an Ingress with a domain name.
i. Deploy the following template to create an Ingress and forward requests to the Service based on the domain name of the Ingress.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - host: demo.domain.ingress.top http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 path: /hello pathType: Prefix
ii. Run the following command to access the Service by using the specified domain name.
Replace ADDRESS with the IP address of the related ALB instance. You can query the IP address by running the
kubectl get ingcommand.curl -H "host: demo.domain.ingress.top" <ADDRESS>/hello
Expected output:
{"hello":"coffee"} -
Create an Ingress without a domain name.
i. Deploy the following template to create an Ingress:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - host: "" http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 path: /hello pathType: Prefix
ii. Run the following command to access the Service without using a domain name:
Replace ADDRESS with the IP address of the related ALB instance. You can query the IP address by running the
kubectl get ingcommand.curl <ADDRESS>/helloExpected output:
{"hello":"coffee"}
ALB Ingresses can forward requests based on URL paths. You can use the pathType parameter to configure different URL match policies. The valid values of pathType are Exact, ImplementationSpecific, and Prefix.
You can perform the following steps to configure different URL match policies.
-
Exact: matches the entire URL path with case sensitivity. Regular expressions are not supported.
i. Deploy the following template to create an Ingress:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo-path namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: - path: /hello backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 pathType: Exact
ii. Run the following command to access the Service:
Replace ADDRESS with the IP address of the related ALB instance. You can query the IP address by running the
kubectl get ingcommand.curl <ADDRESS>/hello
Expected output:
{"hello":"coffee"} -
ImplementationSpecific: the default match policy. Configure the path as a string. If you do not use regular expressions, the policy matches URL paths in the same manner as the
Exactpolicy. Regular expressions that use/*are supported.i. Deploy the following template to create an Ingress:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo-path namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: - path: /hello backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 pathType: ImplementationSpecific
ii. Run the following command to access the Service:
Replace ADDRESS with the IP address of the related ALB instance. You can query the IP address by running the
kubectl get ingcommand.curl <ADDRESS>/helloExpected output:
{"hello":"coffee"} -
Prefix: matches a specified prefix against URL paths. The elements in URL paths are separated by forward slashes (
/). The prefix is case-sensitive and matched against each element of the path.i. Deploy the following template to create an Ingress:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo-path-prefix namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: - path: / backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 pathType: Prefix
ii. Run the following command to access the Service:
Replace ADDRESS with the IP address of the related ALB instance. You can query the IP address by running the
kubectl get ingcommand.curl <ADDRESS>/helloExpected output:
{"hello":"coffee"}
You can use the following annotations to configure health checks for backend server groups.
The following YAML template provides an example on how to configure health checks:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: cafe-ingress
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-enabled: "true"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: "/"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: "HTTP"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-method: "HEAD"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-httpcode: "http_2xx"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: "5"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: "2"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count: "3"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count: "3"
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- http:
paths:
# Configure a context path.
- path: /tea
backend:
service:
name: tea-svc
port:
number: 80
# Configure a context path.
- path: /coffee
backend:
service:
name: coffee-svc
port:
number: 80The following table describes the parameters in the YAML template.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-enabled | Optional. Specifies whether to enable health checks. Default value: true. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path | Optional. The URL based on which health checks are performed. Default value: /. Enter the URL path of the health check page. We recommend that you enter the URL path of a static web page. It must be 1~ to 80 characters in length and can contain letters, digits, hyphens (-), forward slashes (/), periods (.), percent signs (%), question marks (?), number signs (#), and ampersands (&). It can also contain the following extended characters: _ ; ~! ( ) * []@ $ ^ : ' , +. The URL must start with a forward slash (/). By default, to perform health checks, the ALB instance sends HTTP HEAD requests to the default application homepage configured on a backend Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance. The ALB instance sends the requests to the private IP address of the ECS instance. If you do not want to use the default application homepage for health checks, you must specify a URL. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol | Optional. The protocol that is used for health checks. HTTP: The ALB instance sends HEAD or GET requests to a backend server to simulate access from a browser and check whether the backend server is healthy. This is the default protocol. TCP: The system sends SYN packets to a backend server to check whether the port of the backend server is available to receive requests. GRPC: ALB performs gRPC health checks by sending POST or GET requests to a backend server to check whether the backend server is healthy. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-method | Optional. The request method that is used for health checks. HEAD: By default, the ALB instance sends HEAD requests to a backend server to perform HTTP health checks. Make sure that your backend server supports HEAD requests. If your backend servers do not support the HEAD method or the HEAD method is disabled, the health check may fail. In this case, you can use the GET method. POST: By default, gRPC health checks use the POST method. Make sure that your backend servers support POST requests. If your backend servers do not support the POST method or the POST method is disabled, the health check may fail. In this case, you can use the GET method. GET: If the size of a response exceeds 8 KB, the response is fragmented. This does not affect the health check result. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-httpcode | The status codes that are returned when backend servers pass health checks. When the health check protocol is set to HTTP, valid values are http_2xx, http_3xx, http_4xx, and http_5xx. The default value for HTTP health checks is http_2xx. When the health check protocol is set to GRPC, valid values are 0 to 99. Value ranges are supported. You can enter at most 20 value ranges and separate them with commas (,). |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds | The timeout period of a health check. If a backend server, such as an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, does not respond to a probe packet within the specified timeout period, the server fails the health check. Valid values: 1 to 300. Default value: 5. Unit: seconds. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds | The interval between two consecutive health checks. Unit: seconds. Valid values: 1 to 50. Default value: 2. Unit: seconds. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count | The number of times that an unhealthy backend server must consecutively pass health checks before the server is considered healthy. Valid values: 2 to 10. Default value: 3. |
| alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count | The number of times that a healthy backend server must consecutively fail health checks before the server is considered unhealthy. Valid values: 2 to 10. Default value: 3. |
The ALB Ingress controller supports automatic certificate discovery. You must first purchase a certificate in the Certificate Management Service console. Then, specify the domain name of the certificate in the Transport Layer Security (TLS) configurations of the Ingress. This way, the ALB Ingress controller can automatically discover and match the certificate based on the TLS configurations of the Ingress. If you do not want to purchase a certificate during testing, perform the following steps to use a self-signed certificate.
-
Run the following
opensslcommands to create a self-signed certificate. By default, the certificate cannot be verified by the system.openssl genrsa -out albtop-key.pem 4096 openssl req -subj "/CN=demo.alb.ingress.top" -sha256 -new -key albtop-key.pem -out albtop.csr echo subjectAltName = DNS:demo.alb.ingress.top > extfile.cnf openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -sha256 -in albtop.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out albtop-cert.pem -extfile extfile.cnf
-
Upload the certificate in the Certificate Management Service console.
For more information, see Upload a certificate.
-
Add the following setting to the YAML template of the Ingress to specify the domain name in the created certificate:
tls: - hosts: - demo.alb.ingress.topExample:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo-https namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb tls: - hosts: - demo.alb.ingress.top rules: - host: demo.alb.ingress.top http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 path: / pathType: Prefix
-
Run the following command to query the certificate:
curl -v https://demo.alb.ingress.top/You can view the certificate in the output.
* Server certificate: * subject: CN=demo.alb.ingress.top
You can configure an ALB Ingress to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS port 443 by adding the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" annotation.
Example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
name: demo-ssl
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
tls:
- hosts:
- demo.alb.ingress.top
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: demo-service
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
ALB Ingresses support the HTTPS or gRPC protocol. To configure HTTPS or gRPC, add the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "grpc" or alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "https" annotation. If you want to use an Ingress to distribute requests to a gRPC service, you must configure an SSL certificate for the gRPC service and use the TLS protocol to communicate with the gRPC service. Example:
You cannot change the backend protocol. If you need to change the protocol, delete and rebuild the Ingress.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "grpc"
name: lxd-grpc-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
tls:
- hosts:
- demo.alb.ingress.top
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: grpc-demo-svc
port:
number: 9080
ALB Ingresses support rewrite rules. To configure rewrite rules, add the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /path/${2} annotation.
- The ${number} capturing group in the rewrite-target annotation is an advanced feature. To use the feature, submit a ticket.
- In the
rewrite-targetannotation, you must set the type of thepathparameter to Prefix for a capturing group of the${number}type.- By default, when
pathTypeis set to Prefix, characters used for regular expressions are not supported, such as asterisks (*) and question marks (?). To specify characters that are used by regular expressions in the path parameter, you must add therewrite-targetannotation.- The value of the
pathparameter must start with/. This limit applies to Ingress resources.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /path/${2}
name: rewrite-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- path: /something(/|$)(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: demo-service
port:
number: 80
By default, Ingresses expose port 80. You can configure the tls field to expose port 443. You can also configure redirects to listen on port 80 and port 443 at the same time. However, requests to port 80 are redirected by using 301 redirects. If you want to expose other ports, you can add custom annotations.
The following example exposes port 80 and port 443 for the Service:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: cafe-ingress
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]'
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
tls:
- hosts:
- demo.alb.ingress.top
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: demo-service
port:
number: 80Forwarding rules of ALB are matched in sequence. If the match conditions of two forwarding rules overlap, you must add annotations to specify the priorities of the forwarding rules.
For example, Forwarding Rule A matches requests based on the condition path1=/api, and Forwarding Rule B matches requests based on the condition path2=/api/v1. If Forwarding Rule A is matched before Forwarding Rule B, all requests with the prefix /api/v1 are matched by Forwarding Rule A. In this case, you must set the order parameter to configure priorities for the forwarding rules.
The priority of each forwarding rule within a listener must be unique. You can use the
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/orderannotation to specify the priorities of the forwarding rules of an Ingress. Valid values: 1 to 1000. A lower value indicates a higher priority.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: cafe-ingress
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/order: "2"
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: demo-service
port:
number: 80
ALB allows you to configure canary releases based on request headers, cookies, and weights to handle complex traffic routing. You can add the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true" annotation to enable the canary release feature. Then, you can use the following annotations to configure different canary release rules.
Canary releases that use different rules take effect in the following order: header-based > cookie-based > weight-based.
When you perform canary releases to test a new application version, do not modify the original Ingress rules. Otherwise, access to the application may be interrupted. After the new application version passes the test, replace the backend Service used by the earlier application version with the backend Service used by the new application version. Then, delete the Ingress rules for implementing canary releases.
-
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-headerandalb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: This rule matches the headers and header values of requests. You must add both annotations if you want to use this rule.``- If the
headerandheader valueof a request match the rule, the request is routed to the new application version. - If the
headerof a request fails to match theheader-based rule, the request is matched against other types of rules based on the priorities of the rules.
If you set the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header annotation to
location: hz, requests that match the rule are routed to the new application version. Requests that fail to match the rule are routed based on weight-based rules. Example: - If the
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/order: "1"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "location"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "hz"
name: demo-canary
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: demo-service-canary
port:
number: 80
path: /hello
pathType: Prefix-
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie: This rule matches the cookies of requests.- If you set
cookietoalways, requests that match the rule are routed to the new application version. - If you set
cookietonever, requests that match the rule are routed to the old application version.
Cookie-based canary release rules do not support other settings. The cookie value must be
alwaysornever.Requests that contain the
demo=alwayscookie are routed to the new application version. Example:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/order: "2" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie: "demo" name: demo-canary-cookie namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service-hello port: number: 80 path: /hello pathType: Prefix
- If you set
-
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: This rule allows you to set the percentage of requests that are sent to a specified Service. You can enter an integer from 0 to 100.In the following example, the percentage of requests that are routed to the new application version is set to 50%:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/order: "3" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: "50" name: demo-canary-weight namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service-hello port: number: 80 path: /hello pathType: Prefix
ALB Ingresses allow you to configure session persistence by using the following annotations:
-
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session: specifies whether to enable session persistence. Valid values:trueandfalse. Default value:false. -
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session-type: the method that is used to handle a cookie. Valid values:InsertandServer. Default value:Insert.Insert: inserts a cookie. ALB inserts a cookie (SERVERID) into the first HTTP or HTTPS response packet that is sent to a client. The next request from the client contains this cookie and the listener distributes this request to the recorded backend server.Server: rewrites a cookie. When ALB detects a user-defined cookie, it overwrites the original cookie with the user-defined cookie. The next request from the client will contain the user-defined cookie, and the listener will distribute this request to the recorded backend server.
This parameter takes effect when the
StickySessionEnabledparameter is set totruefor the server group. -
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cookie-timeout: specifies the timeout period of cookies. Valid values: 1 to 86400. Default value:1000. Unit: seconds.
Session persistence takes effect on nodes that are added to a backend server group. When a Service of the NodePort type is used, session persistence does not take effect on pods because the ALB network and the pod network do not belong to the same plane. If you set
externalTrafficPolicyof a Service to local, each node is mapped to a pod, and session persistence takes effect on the pods. This applies only to scenarios in which one node hosts one pod. If you want to enable session persistence for pods in all scenarios, you must allocate ENIs to pods. This way, the ALB network and the pod network can be connected.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: cafe-ingress-v3
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session: "true"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session-type: "Insert"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cookie-timeout: "1800"
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- http:
paths:
# Configure a context path.
- path: /tea2
backend:
service:
name: tea-svc
port:
number: 80
# Configure a context path.
- path: /coffee2
backend:
service:
name: coffee-svc
port:
number: 80ALB Ingresses allow you to specify a load balancing algorithms for backend server groups by using the alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-scheduler annotation. Example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: cafe-ingress
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-scheduler: "wlc"
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- host: demo.alb.ingress.top
http:
paths:
- path: /tea
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: tea-svc
port:
number: 80An AlbConfig object is used to configure an ALB instance. The ALB instance can be specified in forwarding rules of multiple Ingresses. Therefore, an AlbConfig object can be associated with multiple Ingresses.
An AlbConfig object is used to configure an ALB instance. If you want to configure multiple ALB instances, you must create multiple AlbConfig objects. Perform the following steps to create an AlbConfig object:
-
Use the following sample code to create an AlbConfig object:
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: alb-demo spec: config: name: alb-test addressType: Internet zoneMappings: - vSwitchId: vsw-uf6ccg2a9g71hx8go**** - vSwitchId: vsw-uf6nun9tql5t8nh15****
Parameter Description spec.config.name The name of the ALB instance. This parameter is optional. spec.config.addressType The type of IP address that the ALB instance uses to provide services. This parameter is required. Valid values: Internet: The ALB instance uses a public IP address. The domain name of the Ingress is resolved to the public IP address of the ALB instance. Therefore, the ALB instance is accessible over the Internet. This is the default value. Intranet: The ALB instance uses a private IP address. The domain name of the Ingress is resolved to the private IP address of the ALB instance. Therefore, the ALB instance is accessible only within the virtual private cloud (VPC) where the ALB instance is deployed. spec.config.zoneMappings The IDs of the vSwitches that are used by the ALB Ingress. You must specify at least two vSwitch IDs and the vSwitches must be deployed in different zones. The zones of the vSwitches must be supported by ALB Ingresses. This parameter is required. For more information about the regions and zones that are supported by ALB Ingresses, see Supported regions and zones. -
Apply the Albconfig object to the cluster.
kubectl apply -f alb-test.yamlExpected output:
AlbConfig.alibabacloud.com/alb-demo created -
Run the following command to confirm that the AlbConfig object is created:
kubectl -n kube-system get AlbConfigExpected output:
NAME AGE alb-demo 87m
You can associate an AlbConfig object with an Ingress by using an IngressClass. To do this, you must first create an IngressClass.
-
Use the following sample code to create an IngressClass.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: IngressClass metadata: name: alb spec: controller: ingress.k8s.alibabacloud/alb parameters: apiGroup: alibabacloud.com kind: AlbConfig name:alb-demo
-
Run the following command to create an IngressClass:
kubectl apply -f alb.yamlExpected output:
ingressclass.networking.k8s.io/alb created -
To associate an AlbConfig object with an Ingress, specify the alb IngressClass in the
ingressClassNamefiled of the Ingress YAML template.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: cafe-ingress spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - http: paths: # Configure a context path. - path: /tea pathType: ImplementationSpecific backend: service: name: tea-svc port: number: 80 # Configure a context path. - path: /coffee pathType: ImplementationSpecific backend: service: name: coffee-svc port: number: 80
To change the name of an AlbConfig object, run the following command. The change is automatically applied after you save the modification.
kubectl -n kube-system edit AlbConfig alb-demo
...
spec:
config:
name: test # The new name that you want to use.
...
To change the vSwitches that are specified for an AlbConfig object, run the following command. The change is automatically applied after you save the modification.
kubectl -n kube-system edit AlbConfig alb-demo
...
zoneMappings:
- vSwitchId: vsw-wz92lvykqj1siwvif****
- vSwitchId: vsw-wz9mnucx78c7i6iog****
...
You can specify a certificate for a listener by specifying the certificate ID in the listeners parameter of the corresponding AlbConfig object. The certificate is used for HTTPS connections. Perform the following steps:
-
Log on to the Certificate Management Service console.
-
In the left-side navigation pane, click SSL Certificates.
-
On the SSL Certificates page, click the Manage Uploaded Certificates tab.
-
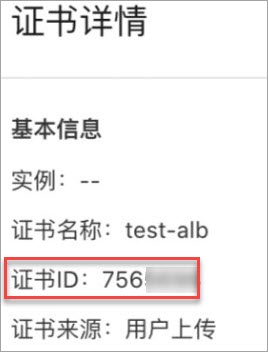
In the Actions column of the certificate that you want to manage, choose ***
* > * Details* ** to obtain the certificate ID.
Example:
-
Modify the AlbConfig YAML file and save the changes.
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: alb-demo spec: config: #... listeners: - caEnabled: false certificates: - CertificateId: 756****-cn-hangzhou IsDefault: true port: 443 protocol: HTTPS #...
The following table describes some of the parameters in the AlbConfig YAML file.
Parameter Description CertificateIdThe ID of the certificate that you want to use. In this example, 756****-cn-hangzhouis specified.756****is the certificate ID that you obtained in the previous step. Format ofCertificateId: If the certificate is created in a region in the Chinese mainland, set the value to756****-cn-hangzhou.-cn-hangzhouis fixed content. You need to only replace756****. If the certificate is created in a region outside the Chinese mainland, set the value to756****-ap-southeast-1.-ap-southeast-1is fixed content. You need to only replace756****.IsDefaultSpecifies whether to set the certificate as the default certificate. In this example, trueis specified. The certificate is set as the default certificate.protocolThe protocol that is used by listeners. In this example, HTTPSis specified. The HTTPS protocol is used by listeners.
-
When you use an AlbConfig object to configure HTTPS listeners, you can specify a TLS security policy. Custom TLS security policies and default TLS security policies are supported. For more information, see TLS security policies.
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: AlbConfig
metadata:
name: alb-demo
spec:
config:
#...
listeners:
- port: 443
protocol: HTTPS
securityPolicyId: tls_cipher_policy_1_1
#...If you want to collect the access logs of ALB Ingresses, set the logProject and logStore parameters in the AlbConfig configuration.
Log Service projects must be manually created. For more information, see Manage projects.
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: AlbConfig
metadata:
name: alb-demo
spec:
config:
accessLogConfig:
logProject: "k8s-log-xz92lvykqj1siwvif****"
logStore: "alb_****"
#...Set logStore to a value that starts with
alb_. If the specified Logstore does not exist, the system automatically creates one with the specified name. (This rule applies only to managed clusters and does not apply to open source clusters.)
After you save the modification to the AlbConfig configuration, you can go to the Log Service console and view the collected log in the specified Logstore.
If you want to reuse an existing ALB instance, specify the ID of the ALB instance in the AlbConfig configuration.
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: AlbConfig
metadata:
name: reuse-alb
spec:
config:
id: ****
forceOverride: false # Specifies whether to overwrite an existing listener: true specifies that the existing listener is forcefully overwritten. false specifies that the existing listener is not overwritten, but listeners that do not conflict with the existing listener are managed. If the existing listener listens on port 80, you can use the Ingress to manage other ports such as 90.
You cannot specify multiple ALB instances for an Ingress. However, you can specify multiple ALB instances for a cluster by specifying different IngressClasses in the spec.ingressClassName field.
-
Create a file named alb-demo2.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: demo spec: config: name: alb-demo2 # The name of an ALB instance. addressType: Internet # The ALB instance has a public IP address. zoneMappings: - vSwitchId: vsw-uf6ccg2a9g71hx8go**** - vSwitchId: vsw-uf6nun9tql5t8nh15****
-
Run the following command to create an AlbConfig object:
kubectl apply -f alb-demo2.yamlExpected output:
AlbConfig.alibabacloud.com/demo created -
Create an alb.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: IngressClass metadata: name: alb-demo2 spec: controller: ingress.k8s.alibabacloud/alb parameters: apiGroup: alibabacloud.com kind: AlbConfig name: demo
-
Run the following command to create an IngressClass:
kubectl apply -f alb.yamlExpected output:
ingressclass.networking.k8s.io/alb-demo2 created -
Specify multiple ALB instances in the
ingressClassNamefield of the Ingress YAML template.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: demo namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb-demo2 rules: - host: "" http: paths: - backend: service: name: demo-service port: number: 80 path: /hello pathType: Prefix
An AlbConfig object is used to configure an ALB instance. Therefore, you can delete an ALB instance by deleting the corresponding AlbConfig object. Before you can delete an AlbConfig object, you must delete all Ingresses that are associated with the AlbConfig object.****
kubectl -n kube-system delete AlbConfig alb-demo
Replace alb-demo with the name of the AlbConfig object that you want to delete.
This topic provides an Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress GlobalConfiguration dictionary to help you identify and troubleshoot configuration format issues. The GlobalConfiguration dictionary contains annotations and AlbConfig fields supported by ALB Ingress.
You can add annotations to ALB Ingress to configure ALB-relevant settings.
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-enabled |
Specifies whether to enable health checks for backend server groups. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path |
The path to which health check requests are sent. | string | "/" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol |
The protocol that is used for health checks. | "HTTP", "TCP" |
"HTTP" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-method |
The health check method. | "HEAD", "POST", "GET" |
"HEAD" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-httpcode |
The status codes used for health checks. | "http_2xx", "http_3xx", "http_4xx", "http_5xx" |
"http_2xx" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds |
The health check timeout in seconds. | 1~300 |
5 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds |
The health check interval. | 1~50 |
2 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count |
The number of times that a server needs to consecutively pass health checks before it is considered healthy. | 2~10 |
3 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count |
The number of times that a server needs to consecutively fail health checks before it is considered unhealthy. | 2~10 |
3 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-connect-port |
The port used for health checks. If you set the value to 0, the port of the backend server will be used for health checks. |
0~65535 |
0 |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect |
Specifies whether to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS requests. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol |
The protocol used by backend server groups. | "http", "https", "grpc" |
"http" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target |
The path that overwrites the path in requests. | string | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports |
Associates listener port with protocol. | jsonObject | '[{"HTTP": 80}]' 或 '[{"HTTPS": 443}]' 或 '[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]' |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/order |
The priorities of forwarding rules. | 1~1000 |
10 |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary |
Specifies whether to enable canary. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header |
Request headers hit when canary is enabled. | string | N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value |
The header value corresponding to the hit request header when canary is enabled. | string | N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie |
The cookie of the requests when canary is enabled. | string | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session |
Specifies whether to enable session persistence. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/sticky-session-type |
The type of session persistence. | "Insert" or "Server" |
"Insert" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cookie-timeout |
The session persistence timeout period in seconds. | 1~86400 |
1000 |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-scheduler |
The load balancing algorithm. | "wrr", "wlc", "sch", "uch" |
"wrr" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-scheduler-uch-value |
This annotation is available when the load balancing algorithm is set to uch. | string | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors |
Specifies whether to enable CORS. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-origin |
The origins from which you want to allow CORS requests. | string | "*" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-expose-headers |
The headers that can be exposed. | stringArray | N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-methods |
The request methods of CORS requests that are allowed. | Select one or more of the following values:["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", "PATCH"] |
"GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-credentials |
Specifies whether to allow credentials in requests. | "true" or "false" |
"true" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-max-age |
The maximum cache time of dryrun requests in the browser. | -1~172800 |
172800 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-headers |
The headers of CORS requests that are allowed. | stringArray | "DNT,X-CustomHeader,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.{svcName} |
The custom forwarding actions. | json | N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/conditions.{svcName} |
The custom forwarding conditions. | json | N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/rule-direction.{svcName} |
The custom forwarding direction. | "Request" or "Response" |
"Request" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-keepalive |
Specifies whether to enable backend persistent connection. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/traffic-limit-qps |
QPS Rate Limiting Configuration. | 1~100000 |
N/A |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex |
Specifies whether regular expressions can be used in the Path field. This annotation is valid only when the path type is Prefix. | "true" or "false" |
"false" |
An AlbConfig is a CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) used to describe an ALB instance and its listeners. The following tables describe the relevant fields.
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
apiVersion |
The API version of the object. | "alibabacloud.com/v1" |
N/A |
kind |
Kind indicates the REST resource corresponding to the object. | "AlbConfig" |
N/A |
metadata |
The metadata of the object. For more information, see metadata。 | ObjectMeta | N/A |
spec |
A list of parameters used to describe the attributes of the ALB instance and its listeners. | AlbConfigSpec | N/A |
status |
The state of the ALB instance will be written into the status field after reconcilation. The value of the field indicates the current status of the ALB instance. |
AlbConfigStatus | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
config |
The attributes of the ALB instance. | LoadBalancerSpec | N/A |
listeners |
The attributes of the listeners of the ALB instance. | []ListenerSpec | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
ALB Instance ID, filling it in indicates enabling the reuse mode. | string |
"" |
name |
The name of the ALB instance. | string |
k8s-{namespace}-{name}-{hashCode} |
addressAllocatedMode |
The address mode of the ALB instance. | "Dynamic" or "Fixed" |
"Dynamic" |
addressType |
The network type of the IPv4 CIDR block of the ALB instance. | "Internet" or "Intranet" |
"Internet" |
ipv6AddressType |
The network type of the IPv6 CIDR block of the ALB instance. | "Internet" or "Intranet" |
"Intranet" |
addressIpVersion |
The protocol version. | "IPv4" or "DualStack" |
"IPv4" |
resourceGroupId |
The ID of the resource group to which the ALB instance belongs. | string | 默认资源组 |
edition |
The feature version of the ALB instance. | "Standard" or "StandardWithWaf" |
"Standard" |
deletionProtectionEnabled |
A reserved field. This field is not adjustable. | *bool |
null |
forceOverride |
Forcefully overwrites the attributes of the ALB instance in reuse mode. | *bool |
false |
listenerForceOverride |
Forcefully overwrites the attributes of the listeners in reuse mode. | *bool |
null |
zoneMappings |
The zone and Elastic IP Address (EIP) configuration. | []ZoneMapping | N/A |
accessLogConfig |
The log collection configuration. | AccessLogConfig | N/A |
billingConfig |
The billing method. | BillingConfig | N/A |
modificationProtectionConfig |
The configuration protection setting. | ModificationProtectionConfig | N/A |
tags |
The tags of the ALB instance. | []Tag | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
vSwitchId |
Required. The vSwitch ID. |
string |
"" |
zoneId |
Automatically specified. The zone of the vSwitch. |
string |
"" |
allocationId |
The ID of the EIP. | string |
"" |
eipType |
A reserved field. | string |
"" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
logStore |
The name of the Simple Log Service Logstore. | string | "" |
logProject |
The name of the Simple Log Service project. | string | "" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
internetBandwidth |
A reserved field. | int | 0 |
internetChargeType |
A reserved field. | string | "" |
payType |
The billing method. | string | "PostPay" |
bandWidthPackageId |
The ID of the associated Internet Shared Bandwidth instance. You cannot disassociate the Internet Shared Bandwidth instance. | string | "" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
reason |
A reserved field. | string |
"" |
status |
A reserved field. | string |
"" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
key |
The key of the tag. | string | "" |
value |
The value of the tag. | string | "" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
gzipEnabled |
Specifies whether to enable compression. | null or true or false |
null |
http2Enabled |
Specifies whether to use HTTP/2. | null or true or false |
null |
port |
Required. The listener port. |
Int Or String | 0 |
protocol |
Required. The listener protocol. |
"HTTP" or "HTTPS" or "QUIC" |
"" |
securityPolicyId |
The ID of the TLS security policy. | string | "" |
idleTimeout |
The idle connection timeout period. A value of 0 indicates that the default value is used. |
int |
60 |
loadBalancerId |
A reserved field. | string | "" |
description |
The name of the listener. | string | ingress-auto-listener-{port} |
caEnabled |
A reserved field. | bool | false |
requestTimeout |
The timeout period of requests. | int | 60 |
quicConfig |
The QUIC listener configuration. | QuicConfig | |
defaultActions |
A reserved field. | []Action |
null |
caCertificates |
A reserved field. | Certificate | null |
certificates |
The listening server certificate. | Certificate | null |
xForwardedForConfig |
The configuration of the XForward header. | XForwardedForConfig | N/A |
logConfig |
A reserved field. | LogConfig |
N/A |
aclConfig |
The access control configuration. | AclConfig | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
quicUpgradeEnabled |
Specifies whether to enable QUIC upgrades. | bool | false |
quicListenerId |
The QUIC listener. | string | "" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
IsDefault |
Specifies whether the current certificate is the default certificate. Each service or system can have only one default certificate. |
bool | false |
CertificateId |
The ID of the certificate. | string | "" |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
XForwardedForClientCertSubjectDNAlias |
The name of the custom header. This field is valid only when XForwardedForClientCertSubjectDNEnabledis set totrue. |
string | "" |
XForwardedForClientCertSubjectDNEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Clientcert-subjectdn header to retrieve information about the owner of the client certificate. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForProtoEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Protoheader to retrieve the listener protocol of the ALB instance. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForClientCertIssuerDNEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Clientcert-issuerdn header to retrieve information about the authority that issues the client certificate. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForSLBIdEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-For-SLB-IDheader to retrieve the ID of the ALB instance. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForClientSrcPortEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Client-Portheader to retrieve the client port. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForClientCertFingerprintEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Clientcert-fingerprintheader to retrieve the fingerprint of the client certificate. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Forheader to retrieve client IP addresses. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForSLBPortEnabled |
Specifies whether to use theX-Forwarded-Port header to retrieve the listener ports of the ALB instance. |
bool | false |
XForwardedForClientCertClientVerifyAlias |
The name of the custom header. This field is valid only whenXForwardedForClientCertClientVerifyEnabledis set to true. |
string | "" |
XForwardedForClientCertIssuerDNAlias |
The name of the custom header. This field is valid only when XForwardedForClientCertIssuerDNEnabledis set totrue. |
string | "" |
XForwardedForClientCertFingerprintAlias |
The name of the custom header. This field is valid only whenXForwardedForClientCertFingerprintEnabledis set totrue. |
string | "" |
XForwardedForClientCertClientVerifyEnabled |
Specifies whether to use the X-Forwarded-Clientcert-clientverifyheader to retrieve the verification result of the client certificate. |
bool | false |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
aclName |
The name of the ACL policy associated in AclEntry mode. | string | N/A |
aclType |
The ACL policy type, black and white list. | "" or Black or White |
"" |
aclEntries |
The ACL policy entry. | []string | null |
aclIds |
The ID of an existing ACL policy. | []string | null |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
loadBalancer |
The status of the ALB instance. | LoadBalancerStatus | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
dnsname |
The status of the ALB instance. | string | N/A |
id |
The ID of the ALB instance. | string | N/A |
listeners |
The attributes of the listeners. | []ListenerStatus | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
portAndProtocol |
The listener port and protocol configuration. | string | 80/HTTP |
certificates |
The associated certificates. | []AppliedCertificate | N/A |
| Annotation | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
certificateId |
The ID of the certificate. | string | xxxx-cn-hangzhou |
isDefault |
Specifies whether the certificate is the default certificate. | bool | true |