-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 10
/
Copy pathREADME.Rmd
196 lines (123 loc) · 7.17 KB
/
README.Rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
---
output: github_document
editor_options:
chunk_output_type: console
---
<!-- README.md is generated from README.Rmd. Please edit that file -->
```{r, echo = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
warning = FALSE,
fig.path = "man/figures/README-"
)
```
# easyalluvial <a href='https://erblast.github.io/easyalluvial'><img src='man/figures/logo.png' align="right" height="139" /></a>
[](https://github.com/erblast/easyalluvial/actions)
[](https://codecov.io/github/erblast/easyalluvial?branch=master)
[](https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=easyalluvial)
[](https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=easyalluvial)
[](https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=easyalluvial)
Alluvial plots are similar to [sankey diagrams](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sankey_diagram) and visualise categorical data over multiple dimensions as flows. [Rosval et. al. 2010](https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0008694) Their graphical grammar however is a bit more complex then that of a regular x/y plots. The [`ggalluvial`](http://corybrunson.github.io/ggalluvial/) package made a great job of translating that grammar into [`ggplot2`](https://github.com/tidyverse/ggplot2) syntax and gives you many option to tweak the appearance of an alluvial plot, however there still remains a multi-layered complexity that makes it difficult to use 'ggalluvial' for explorative data analysis. 'easyalluvial' provides a simple interface to this package that allows you to produce a decent alluvial plot from any dataframe in either long or wide format from a single line of code while also handling continuous data. It is meant to allow a quick visualisation of entire dataframes with a focus on different colouring options that can make alluvial plots a great tool for data exploration.
## Features
- plot alluvial graph with a single line of code of a given dataframe
- support for wide and long data format [(wiki, wide vs. long/narrow data)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wide_and_narrow_data)
- automatically transforms numerical to categorical data
- helper functions for variable selection
- convenient parameters for coloring and ordering
- marginal histograms
- **model agnostic partial dependence and model response alluvial plots with 4 dimensions**
- **[interactive plots with `easyalluvial` and `parcats`](https://erblast.github.io/parcats/articles/parcats.html)**
## Installation
### CRAN
```{r cran, eval = FALSE }
install.packages('easyalluvial')
```
### Development Version
```{r gh-installation, eval = FALSE}
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("erblast/easyalluvial")
```
## Documentation
- [pkgdown website](https://erblast.github.io/easyalluvial/)
* [Data Exploration with Alluvial Plots](https://erblast.github.io/easyalluvial/articles/data_exploration.html)
* [Visualising Model Response ](https://erblast.github.io/easyalluvial/articles/model_response.html)
* [Interactive Plots with parcats](https://erblast.github.io/easyalluvial/articles/parcats.html)
## Examples
```{r}
suppressPackageStartupMessages( require(tidyverse) )
suppressPackageStartupMessages( require(easyalluvial) )
```
### Alluvial from data in wide format
#### Sample Data
```{r wide}
knitr::kable( head(mtcars2) )
```
#### Plot
Continuous Variables will be automatically binned as follows.
- High, High (HH)
- Medium, High (MH)
- Medium (M)
- Medium, Low (ML)
- Low, Low (LL)
```{r wide_plot }
alluvial_wide( data = mtcars2
, max_variables = 5
, fill_by = 'first_variable' )
```
### Alluvial from data in long format
#### Sample Data
```{r long}
knitr::kable( head(quarterly_flights) )
```
#### Plot
```{r plot_long}
alluvial_long( quarterly_flights
, key = qu
, value = mean_arr_delay
, id = tailnum
, fill = carrier )
```
### Marginal Histograms
```{r}
alluvial_wide( data = mtcars2
, max_variables = 5
, fill_by = 'first_variable' ) %>%
add_marginal_histograms(mtcars2)
```
### Interactive Graphs
```{r eval = F}
suppressPackageStartupMessages( require(parcats) )
p = alluvial_wide(mtcars2, max_variables = 5)
parcats(p, marginal_histograms = TRUE, data_input = mtcars2)
```
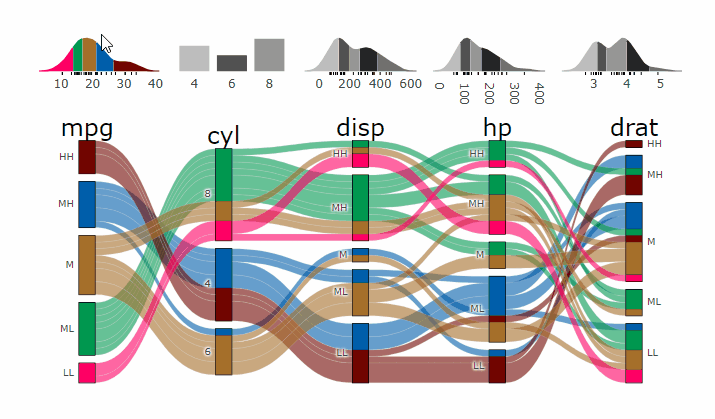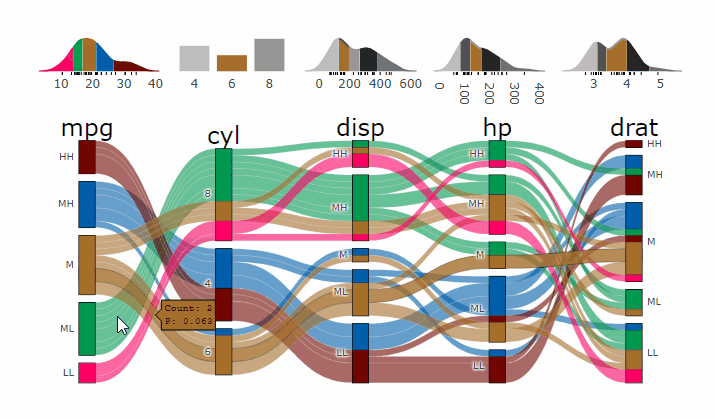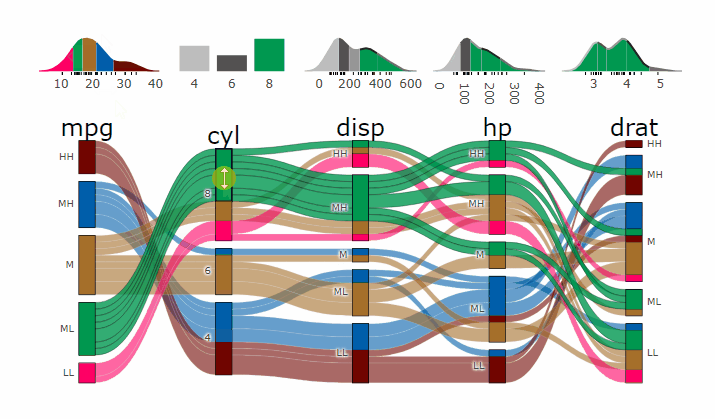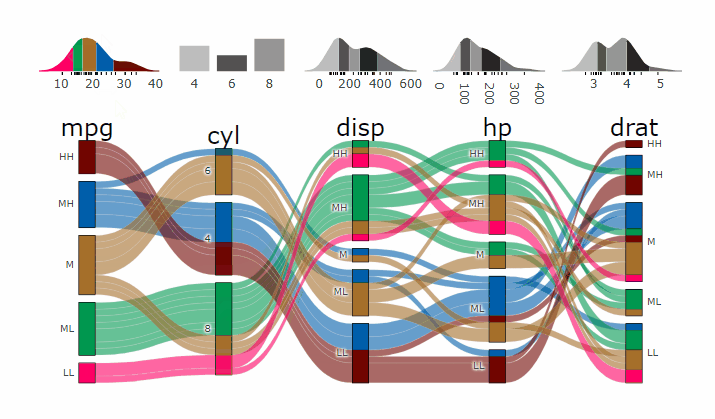
- **[Live Widget](https://erblast.github.io/parcats/articles/parcats.html)**
### Partial Dependence Alluvial Plots
Alluvial plots are capable of displaying higher dimensional data on a plane, thus lend themselves to plot the response of a statistical model to changes in the input data across multiple dimensions. The practical limit here is 4 dimensions while conventional partial dependence plots are limited to 2 dimensions.
Briefly the 4 variables with the highest feature importance for a given model are selected and 5 values spread over the variable range are selected for each. Then a grid of all possible combinations is created. All none-plotted variables are set to the values found in the first row of the training data set. Using this artificial data space model predictions are being generated. This process is then repeated for each row in the training data set and the overall model response is averaged in the end. Each of the possible combinations is plotted as a flow which is coloured by the bin corresponding to the average model response generated by that particular combination.
- [more on partial dependence plots (ebook)](https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/)
- [Tutorial](https://www.datisticsblog.com/2019/04/visualising-model-response-with-easyalluvial/)
`easyalluvial` contains wrappers for `parsnip` and `caret` models. Custom Wrappers for other models can easily be created.
```{r fig.width=12, fig.height= 9}
df = select(mtcars2, -ids)
m = parsnip::rand_forest(mode = "regression") %>%
parsnip::set_engine("randomForest") %>%
parsnip::fit(disp ~ ., df)
p = alluvial_model_response_parsnip(m, df, degree = 4, method = "pdp")
p_grid = add_marginal_histograms(p, df, plot = F) %>%
add_imp_plot(p, df)
```
### Interactive Partial Dependence Plot
```{r eval = F}
parcats(p, marginal_histograms = TRUE, imp = TRUE, data_input = df)
```
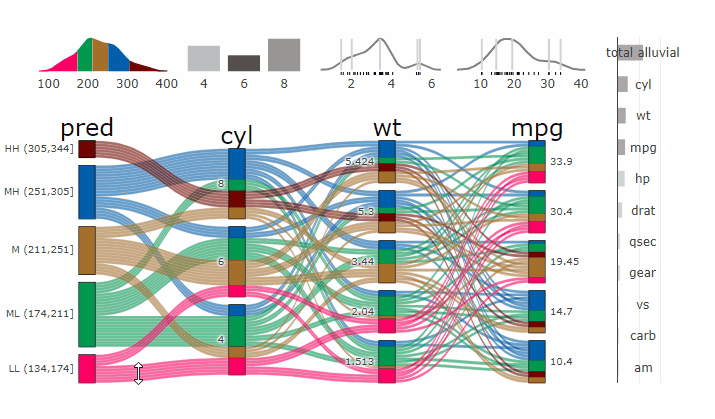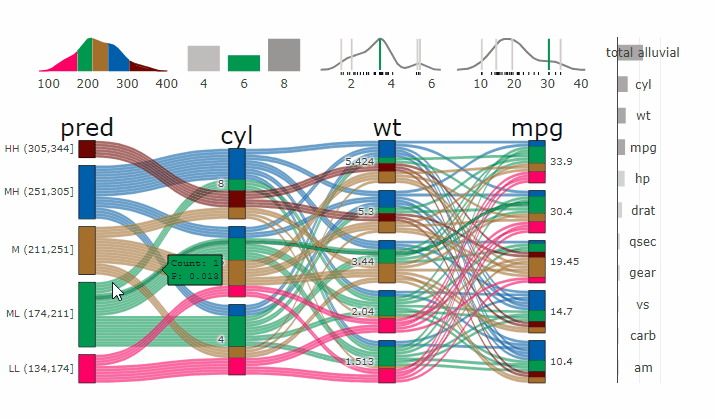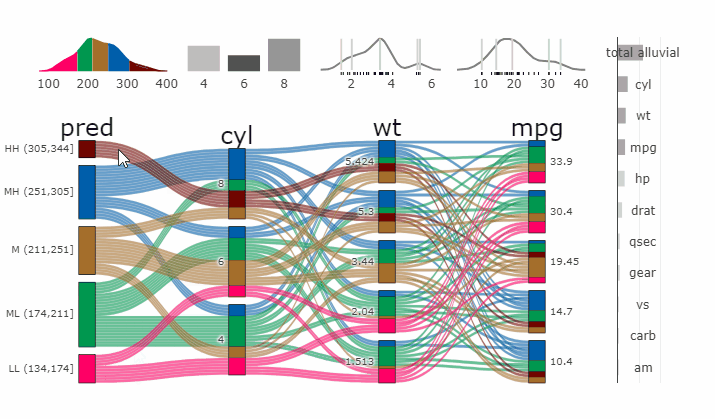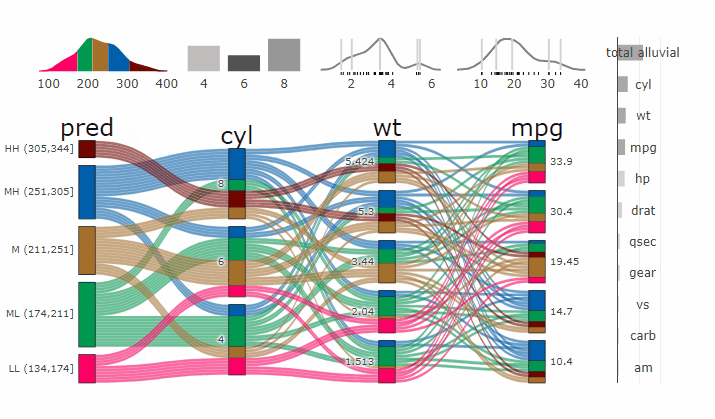
- **[Live Widget](https://erblast.github.io/parcats/articles/parcats.html)**
# ClinicoPath {jamovi} Module
[ClinicoPath jamovi Module](https://github.com/sbalci/ClinicoPathJamoviModule) (thanks to Serdar Balci) adds `easyalluvial` plots to `jamovi`a spreadsheet interface for doing statistics with `R`.
# Similar Packages
- [`ggalluvial`](https://github.com/corybrunson/ggalluvial/)
- [`alluvial`](https://github.com/mbojan/alluvial)
- [`networkD3`](https://github.com/christophergandrud/networkD3)
- [`ggbump`](https://github.com/davidsjoberg/ggbump)