This script automatically creates snapshots of your Hetzner Cloud Servers and deletes the old ones.
Snapshots then work like the automatic backups offered directly by Hetzner, with the advantage that more backups and at self-defined times can be created.
For ease of use, the script works with the powerful labels directly in the Hetzner Cloud Console. Just add labels to the servers and you are done.
1. Run the docker image
docker run -d --name hcloud-snapshot-as-backup \
--restart unless-stopped \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
-e API_TOKEN= \
-e SNAPSHOT_NAME="%name%-%timestamp%" \
-e LABEL_SELECTOR="AUTOBACKUP" \
-e KEEP_LAST=3 \
-e CRON="0 1 * * *" \
fbrettnich/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup
Put your Hetzner Cloud Console API-Key after API_TOKEN= in line 4.
Optional: Set CRON to false to disable CronScheduler in the container and schedule outside of the container, especially for using services like Amazon ECS scheduled tasks or Google Cloud Run jobs.
1. Download docker-compose.yml
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fbrettnich/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup/main/docker-compose.yml > docker-compose.yml
2. Edit configuration
Open the docker-compose.yml file to complete the configuration.
You can find more information about the configuration below (click here)
3. Run docker-compose
docker-compose up -d
1. Clone this repository
apt install git
git clone https://github.com/fbrettnich/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup.git /opt/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup
2. Install requirements
apt install python3 python3-pip
pip3 install -r /opt/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup/requirements.txt
3. Copy config.json
cd /opt/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup/
cp config-example.json config.json
4. Edit configuration
Open the config.json file to complete the configuration.
You can find more information about the configuration below (click here)
5. Run script
python3 /opt/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup/snapshot-as-backup.py
To execute the script automatically, you can create a crontab: Crontab Generator
crontab -e
Add the crontab at the end of the file:
0 1 * * * python3 /opt/hcloud-snapshot-as-backup/snapshot-as-backup.py >/dev/null 2>&1
This crontab executes the script every day at 1am.
Depending on how you run the script, you will need to configure.
When you run the script using Docker, the options are set by environment variables.
When you run the script via command/crontab, the options are set via the configuration file (config.json).
- Login to Hetzner Cloud Console
- Select your project
- Click "Access" on the left side
- Switch to "API-Tokens" at the top
- Click on "Create API Token" and create a new token with read & write permission
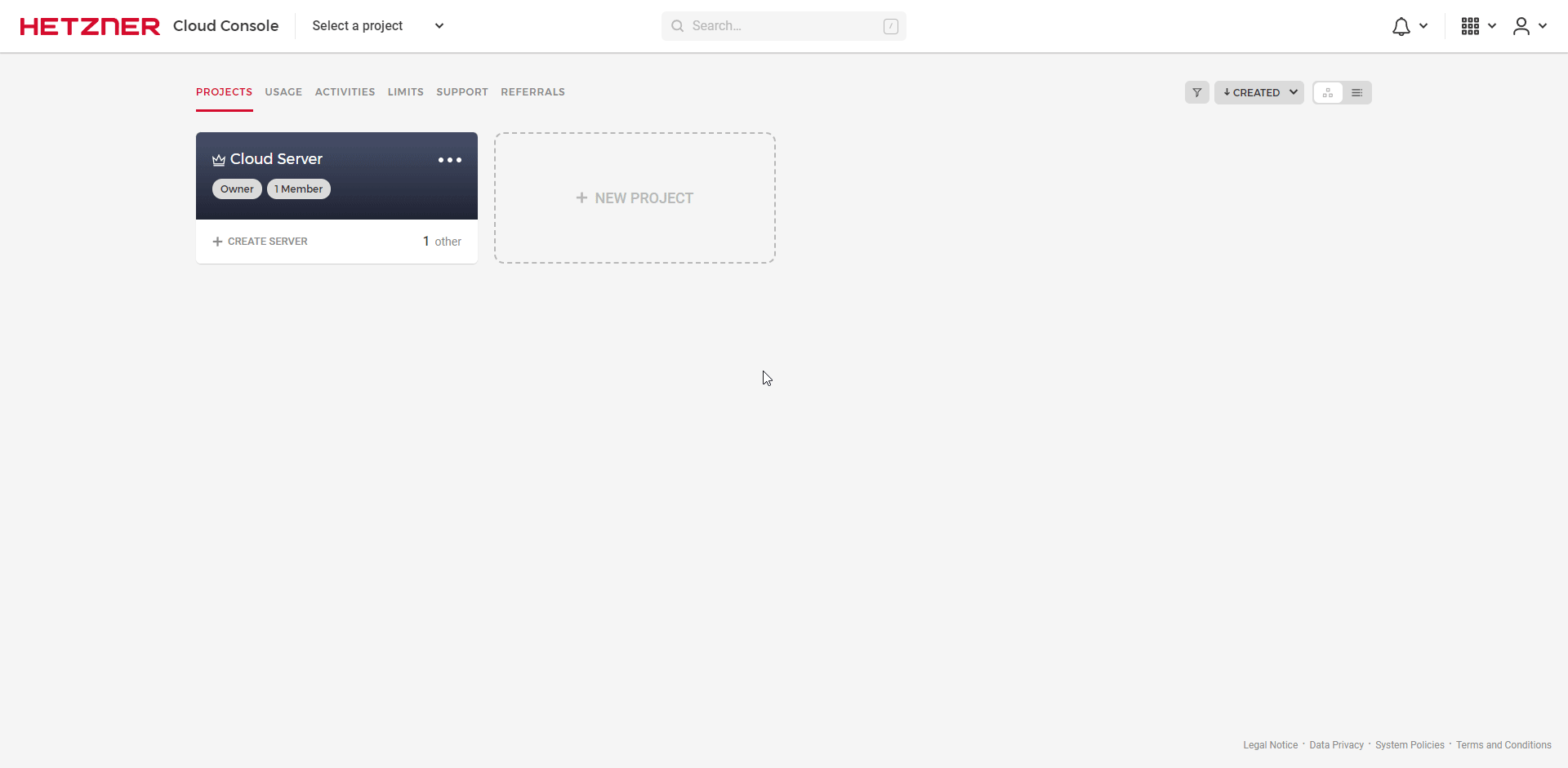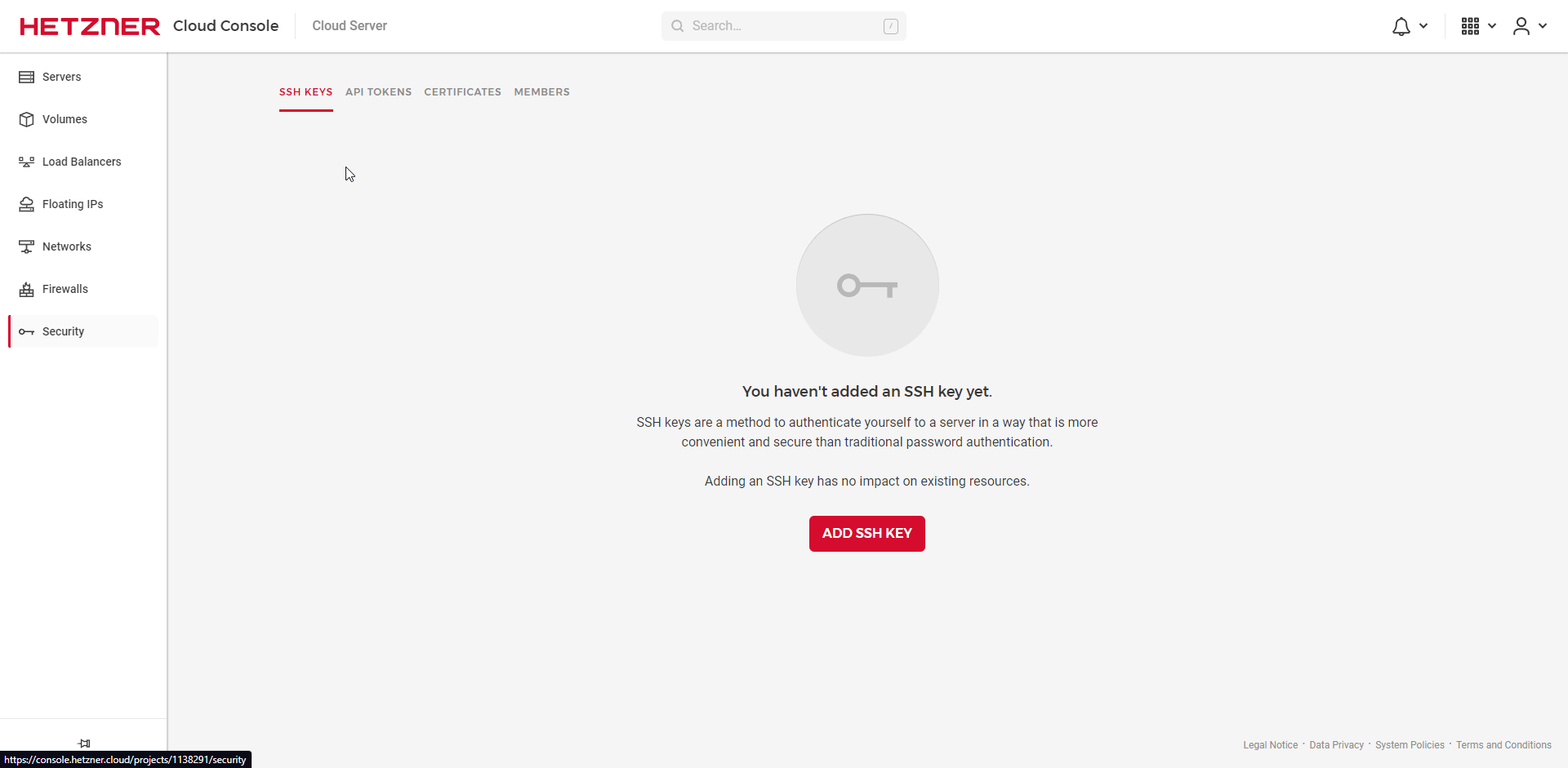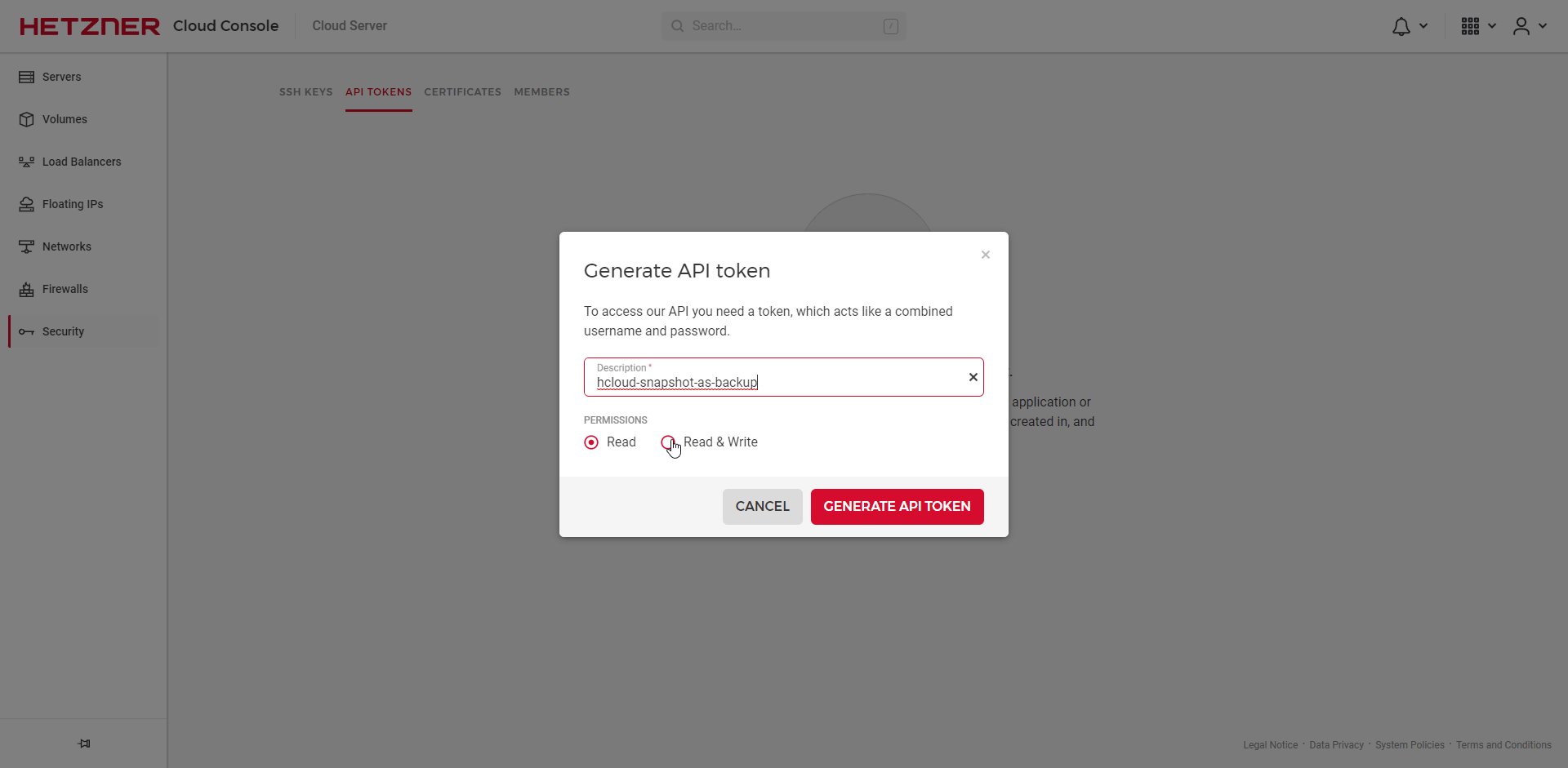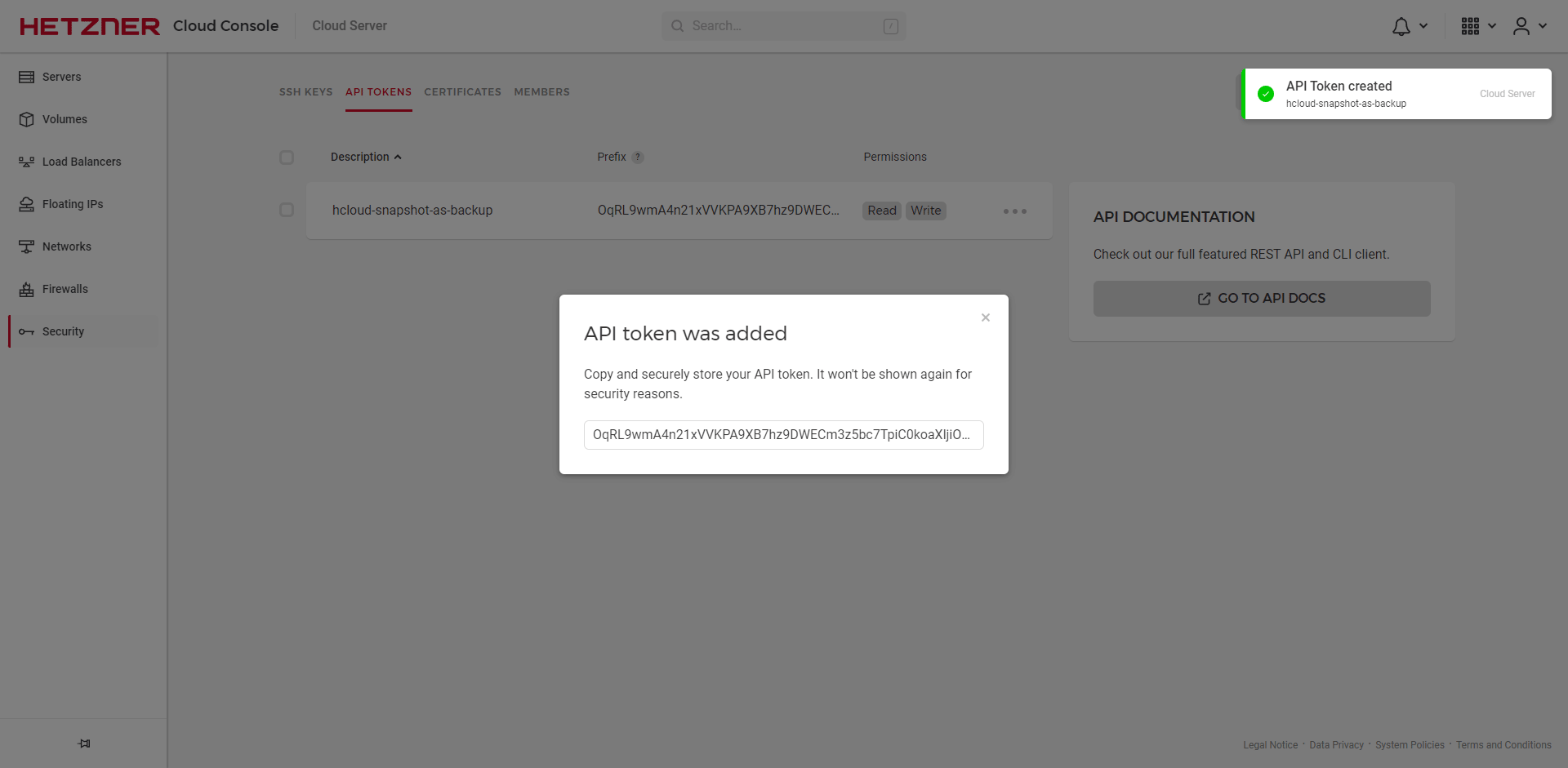
- Copy the key and paste it into the environment variables under
API_TOKENor in the config underapi-token
You can specify in the environment variables under KEEP_LAST or in the config under keep-last how many backups you want to keep per server by default.
Labels can be used to overwrite the default value directly in the Hetzner Cloud Console.
Add the label AUTOBACKUP.KEEP-LAST with the value that should apply to the server.
The newest ones are kept and old ones are deleted.
All servers that should be included by the script and automatic snapshot backups should be created must have the label AUTOBACKUP with the value true.
You can change the default label from AUTOBACKUP to something else by changing the label_selector value in the config. If in a docker environment you can set the LABEL_SELECTOR environment variable. When changing the label_selector, you must also use this for the KEEP-LAST setting.
Specify how you want your snapshots to be named in the environment variables under SNAPSHOT_NAME or under snapshot-name in the config.
By default they are named <server name>-<timestamp>.
| Placeholder | Value |
|---|---|
| %id% | ID of the server |
| %name% | Name of the server |
| %timestamp% | Current timestamp |
| %date% | Current date (%Y-%m-%d) |
| %time% | Current time (%H:%M:%S) |
If you run the script in Docker, a cron may be specified in the environment variables under CRON.
The cron is used to define how often and at which times the script should be executed.
Optionally, set CRON to false to disable CronScheduler in the container and schedule outside of the container.
Here you can create a cron: Cron Generator
For example:
0 1 * * *
This cron executes the script every day at 1am.
This script works with the powerful Hetzner Labels.
- Server
AUTOBACKUP- Server with label
AUTOBACKUPand valuetrueare included by the script - This makes it possible to specify directly in the Hetzner Cloud Console for which servers automatic snapshot backups should be created
- Server with label
AUTOBACKUP.KEEP-LAST(optional)- The label
AUTOBACKUP.KEEP-LASTcan be used to specify how many backups should be kept for this server - If this label is not specified, the default value from the config is used
- The label
- Snapshots
AUTOBACKUP- Snapshots are provided with the label
AUTOBACKUP - This makes it possible to see which snapshot was automatically created by the script
- The script ignores all snapshots without this label (Therefore, only old snapshots with this label are deleted)
- If you want to keep an automatically generated snapshot, just remove the label
AUTOBACKUP
- Snapshots are provided with the label
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Snapshot Backups can be created at own times (Backups at given time) | Snapshots are limited (but higher limit can be requested) |
| Any number can be kept (Backups only maximum 7) | May be more expensive for extremely large servers (lots of storage) |
| Are cheaper than backups for smaller servers (less storage space) | |
| Are not server bound (Backups will be deleted if you delete the cloud server) | |
| New servers can be created directly from the snapshot | |
| Snapshots are stored in a different location (same network zone) than the cloud server (Backups only in the same location as the cloud) | |
| Snapshots can be moved to another project |