An AI model to remove the specific noise from the noisy input audio using the essentials of Deep Learning.
A deep learning model is used to take input audio and detect the type of noises present in the audio. Then, a 'noise reducer' is used to remove the similar kind of audio from the input file and creats a noise free clean audio file.
Dataset used is: UrbanSound8K
Dataset Size: 6GB
Contains predefined 10-fold most common noises, stated below:
air_conditioner
car_horn
children_playing
dog_bark
drilling
engine_idling
gun_shot
jackhammer
siren
street_music
model : Saved model
noise : contains 10 type of noise samples
results : contains the resulted clean audio
sample_dataset : contains 54 audio samples from the dataset
test_audio : audios used for testing performance
UrbanSound8K : metadata file for the real audio along with it's labels
preprocess.py : Contains the preprocessing performed on the data:
- converting audio file into spectrogram
- Spectro to mfcc
- Feature extraction on melspectrograms
- reshaping to 2D to CSV form
- train/test split and save as csv
train.py : - Retrieve the data from csv
- Reshape to One Hot to CNN required form
- Model formation and compilation
- Saving model with test score
test.py : - Loads model
- Inputs audio file and Preprocess
- Predict the NOISE present
- Removes corresponding noises using 'noise reducer'
- Saves the final output
1. python3 preprocess.py
2. pyhton3 train.py
3. python3 test.py
The training and testing of the model was done on the server with :
60GB RAM
16GB GPU
Training duration: 3 min for 40 epochs, 50 batch size.
Training Accuracy: 97.1% Training Loss: 0.07
Validation Accuracy: 79.5% Validation Loss: 0.4
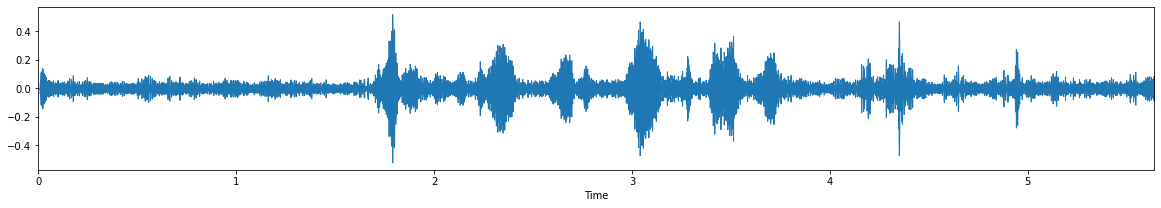
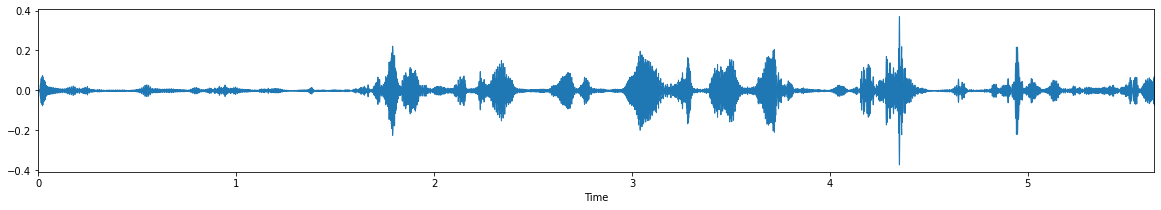
Input Audio 1: noisy-1.wav
Result : cleaned-1.wav
input audio:
output :
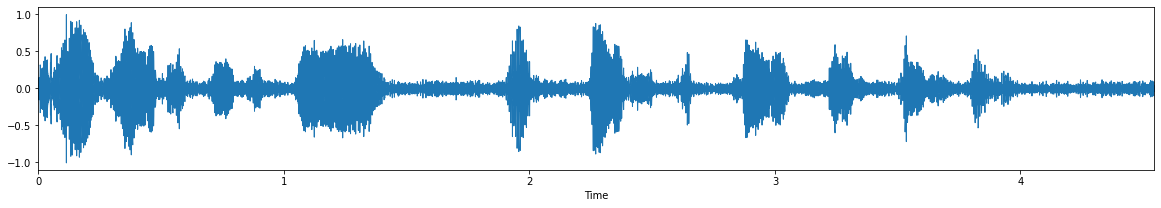
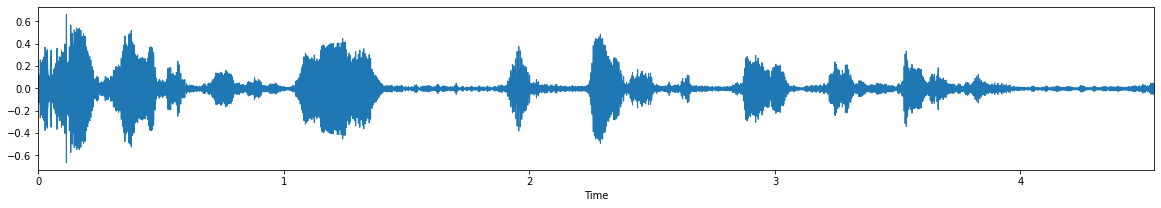
Input Audio 2: noisy-2.wav
Result : cleaned-2.wav
input audio:
output :
Results obtained are remarkable, still a number of things can be done to improve the performance:
- Reduction in real audio loss using HQ filters
- Increase number of noise-removal sample to get more accurate results.
- More generalized method of filtering can be performed.
- Do ping for quality updates and ideas.