- Interact with the user about their health.
- Understand their symptoms.
- Provide a diagnosis.
- Chatbot as a service platforms such as Google DialogFlow and Rasa.
- Custom models.
-
Modules-based models: The chatbot engine is distributed into multiple models each responsible for a certain task. Typical architecture:
- Intent classifier. For example, given “What are the symptoms of COVID-19?”, the intent of this question would be something like “symptoms_questionnaire”.
- Named-entity recognition. For the above example, an entity would be “COVID-19”.
- Responder. Given and intent and named entities, return hard-coded or retrieved response.
-
End-to-end models: Models that take a message as input and produce a reply as output. Possible such model implementations:
-
Sequence-to-sequence models:
-
Encoder-decoder architecture: This model learns a mapping between a message and its response.
-
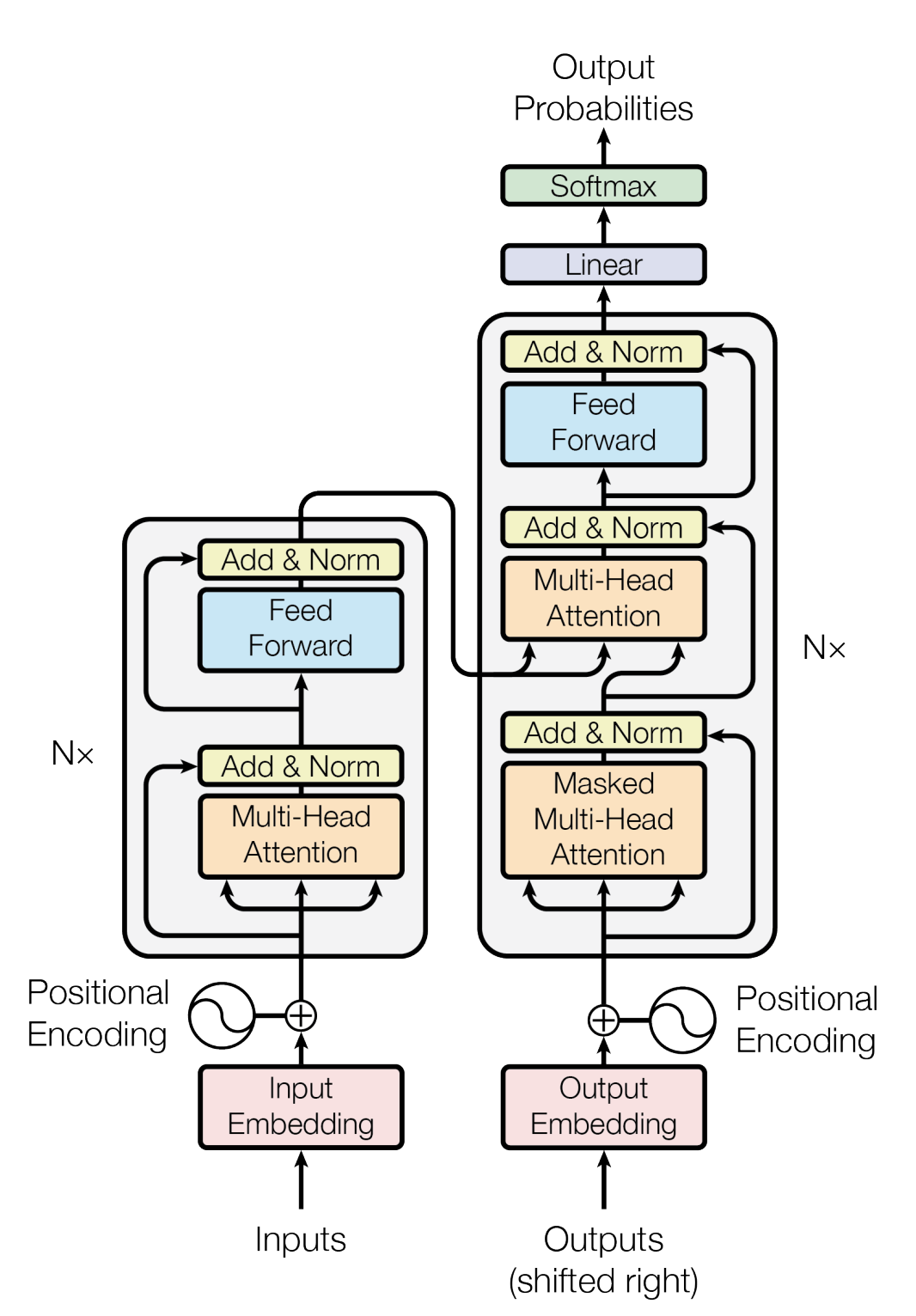
The more advanced Transformer architecture: Compared to the previous model, it’s better in that it:
- Allows parallelization, thus it’s faster.
- Has an additional positional encoder after the input embedder which adds context based on the position of the word.
- Uses the Attention mechanism that decides what part of the sentence should be focused on.
-
-
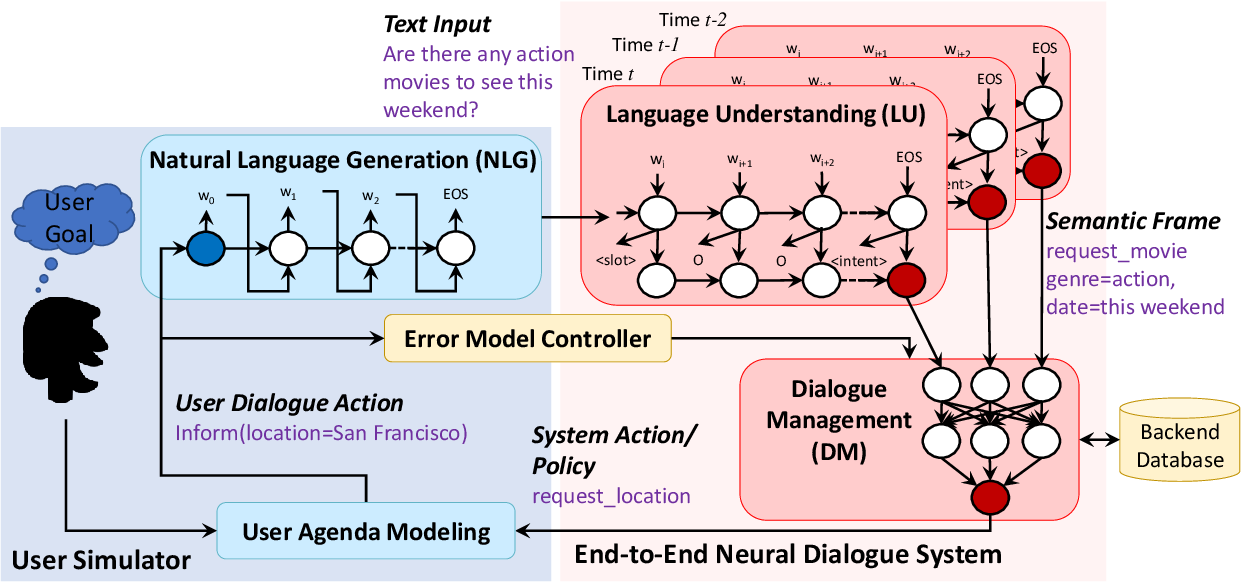
The more promising Task-Oriented Dialogue System:
Limitations with the previous models:
- Require a lot of training data.
- Don’t preserve chat context, because it only learns a mapping between a message and its response.
This approach solves the above problems by introducing a dialog manager with a policy trained via a deep reinforcement learning technique. This manager is responsible for two things:
- Dialog state tracking: The component responsible for tracking what the user wanted throughout the chat (preserves context).
- Dialog policy managing: The component responsible for deciding whether to prompt the user for more information or retrieving the complete user request from an Information Retrieval system.
We could seek a model that uses the Transformer architecture in this system.
-
-
-
If we are to implement a task-oriented system, we would need dialog data, and in that instance, we could use MedDialog and such datasets after translating them to Arabic if needed:
MedDialog is an accumulation of two large-scale medical dialog datasets in English and Chinese. The English dataset contains 0.3 million conversations between patients and doctors and 0.5 million utterances, and the Chinese one has 1.1 million conversations and 4 million utterances.
-
And if we are to go the sequence-to-sequence route, we could use WebTeb and such websites after scraping them.
These websites also could serve as a good source of info for the Information Retrieval system component of the task-oriented dialog system.
-
Data augmentation. For example, building templates of logically and clinically verified questions and augmenting them with data scrapped online.
-
OlloBot: A text-based Arabic health conversational agent.
OlloBot uses IBM Watson Assistant and can only converse about six pre-defined topics that the user has to select one from before starting the conversation.
-
Enterprise commercial applications such as botpress and botter. They follow a modules-based approach where responses defined by the customers are retrieved after defining the user’s intent and message entities.
-
The research paper Intelligent Arabic-Based Healthcare Assistant.
We mainly aim to use services such as Telegram, WhatsApp, or Messenger as our user interface. And possibly develop our own interface later.
- Scheduling.
- Collecting patients’ input.
- Insurance inquiries.
- Requesting prescription refills.