Unified Realtime/API framework for .NET platform and Unity.
📖 Documentation (English) | Documentation (Japanese)
MagicOnion is a modern RPC framework for .NET platform that provides bi-directional real-time communications such as SignalR and Socket.io and RPC mechanisms such as WCF and web-based APIs.
This framework is based on gRPC, which is a fast and compact binary network transport for HTTP/2. However, unlike plain gRPC, it treats C# interfaces as a protocol schema, enabling seamless code sharing between C# projects without .proto (Protocol Buffers IDL).
Interfaces are schemas and provide API services, just like the plain C# code
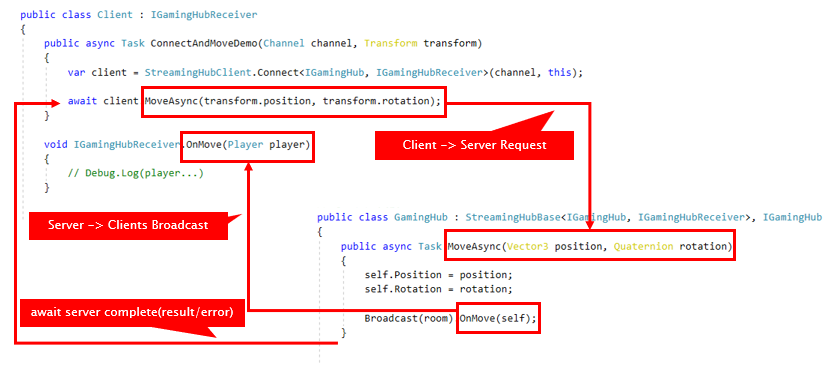
Using the StreamingHub real-time communication service, the server can broadcast data to multiple clients
MagicOnion can be adopted or replaced in the following use cases:
- RPC services such as gRPC, used by Microservices, and WCF, commonly used by WinForms/WPF
- API services such as ASP.NET Core Web API targeting various platforms and clients such as Windows WPF applications, Unity games, .NET for iOS, Android, and .NET MAUI
- Bi-directional real-time communication such as Socket.io, SignalR, Photon and UNet
MagicOnion supports API services and real-time communication, making it suitable for various use cases. You can use either of these features separately, but configurations that combine both are also supported.
More information about MagicOnion can be found in the MagicOnion documentation.
MagicOnion is designed to run on various .NET platforms. The requirements for the server and client are as follows.
MagicOnion server requires .NET 8+.
MagicOnion client supports a wide range of platforms, including .NET Framework 4.6.1 to .NET 8 as well as Unity.
- .NET 8+
- .NET Standard 2.1, 2.0
- Unity 2022.3 (LTS) or newer
- Windows, macOS, iOS, Android
- IL2CPP, Mono
This guide shows how to create a simple MagicOnion server and client. The server provides a simple service that adds two numbers, and the client calls the service to get the result.
MagicOnion provides RPC services like Web API and StreamingHub for real-time communication. This section implements an RPC service like Web API.
At first, create a MagicOnion server project and define and implement a service interface.
To start with a Minimal API project (see: Tutorial: Create a minimal web API with ASP.NET Core), create a project from the ASP.NET Core Empty template. Add the NuGet package MagicOnion.Server to the project. If you are using the .NET CLI tool to add it, run the following command:
dotnet add package MagicOnion.ServerOpen Program.cs and add some method calls to Services and app.
using MagicOnion;
using MagicOnion.Server;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddMagicOnion(); // Add this line(MagicOnion.Server)
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapMagicOnionService(); // Add this line
app.Run();At this point, you are ready to use MagicOnion in your server project.
Add the IMyFirstService interface to share it between the server and the client. In this case, the namespace that contains the shared interface is MyApp.Shared.
The return type must be UnaryResult<T> or UnaryResult, which is treated as an asynchronous method like Task or ValueTask.
using System;
using MagicOnion;
namespace MyApp.Shared
{
// Defines .NET interface as a Server/Client IDL.
// The interface is shared between server and client.
public interface IMyFirstService : IService<IMyFirstService>
{
// The return type must be `UnaryResult<T>` or `UnaryResult`.
UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y);
}
}Add a class that implements the IMyFirstService interface. The client calls this class to process the request.
using MagicOnion;
using MagicOnion.Server;
using MyApp.Shared;
namespace MyApp.Services;
// Implements RPC service in the server project.
// The implementation class must inherit `ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>` and `IMyFirstService`
public class MyFirstService : ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>, IMyFirstService
{
// `UnaryResult<T>` allows the method to be treated as `async` method.
public async UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Received:{x}, {y}");
return x + y;
}
}The service definition and implementation are now complete.
It is now ready to start the MagicOnion server. You can start the MagicOnion server by pressing the F5 key or using the dotnet run command. At this time, note the URL displayed when the server starts, as it will be the connection destination for the client.
Create a Console Application project and add the NuGet package MagicOnion.Client.
Share the IMyFirstService interface and use it in the client. You can share the interface in various ways, such as file links, shared libraries, or copy & paste...
In the client code, create a client proxy using MagicOnionClient based on the shared interface and call the service transparently.
At first, create a gRPC channel. The gRPC channel abstracts the connection, and you can create it using the GrpcChannel.ForAddress method. Then, create a MagicOnion client proxy using the created channel.
using Grpc.Net.Client;
using MagicOnion.Client;
using MyApp.Shared;
// Connect to the server using gRPC channel.
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:5001");
// Create a proxy to call the server transparently.
var client = MagicOnionClient.Create<IMyFirstService>(channel);
// Call the server-side method using the proxy.
var result = await client.SumAsync(123, 456);
Console.WriteLine($"Result: {result}");Tip
When using MagicOnion client in Unity applications, see also Works with Unity.
More information about MagicOnion can be found in the MagicOnion documentation.
This library is under the MIT License.