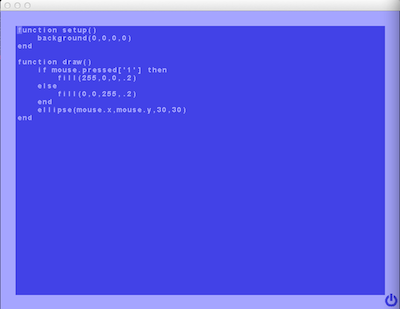
Codakido is an attempt at creating a Codea-inspired environment to teach children how to write Lua programs. It features a graphical programming environment and a Commdore-64 style integrated editor so that the programmer is confined into a friendly environment with a simple editor:
The following is a screenshot of the running program. The programmer can currently switch between edit and play mode pressing the ESC key.
Codakido is written in ANSI C and uses SDL, so should compile on Mac OS X, Linux and Windows without issues.
The coordinate system and the basic drawing functions are compatible with Codea (check http://twolivesleft.com/Codea/ for more information), but there is no support for stroke.
There is no aim at Codea compatibility, but who is familiar with Codea should feel at home with CodaKido in terms of API and structure of the program.
I wrote it mainly because I and my children have fun with Codea but we don't have an iPad at home, and using a real keyboard sometimes can be less frustrating.
Start codakido with:
./codakido example.lua
To switch between program and editor mode press the ESC key.
Check the "examples" folder for small examples.
Similar to Codea drawing primitives:
- fill(r,g,b,alpha): select the drawing color.
- background(r,g,b): paint the whole background with the specified color.
- rect(x,y,width,height): draw a rectangle at x,y (left-bottom corner).
- ellipse(x,y,width,height): draw an ellipse centered at x,y.
- line(x1,y1,x2,y2): draw a line from x1,y1 to x2,y2.
- text(x,y,string): print the specified text at x,y using a bitmap font.
Not available in Codea:
- triangle(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3): draw a triangle with the specified vertex.
To check if a key 'a' is pressed use:
if keyboard.pressed['a'] then ...
SDL Key symbol names are used. You can easily find how a given key is called using the following Lua program:
function draw()
for k,v in pairs(keyboard.pressed) do
print(k)
end
end
(You can find this program under the examples folder).
It is also possible to trap low level SDL events accessing keyboard.state and keyboard.key fields of the keyboard table.
keyboard.state is one of:
"down" -> KEYDOWN event
"up" -> KEYUP event
"none" -> No event
keyboard.key is set to the key pressed or released when state is different than "none".
mouse.x and mouse.y gives you the current mouse coordinates. To check if a button is pressed use:
if mouse.pressed['1'] then ...
Mouse buttons are called '1', '2', '3', ... and so forth.
Codakido was written by Salvatore Sanfilippo and is released under the BSD two-clause license, see the COPYING file for more information.