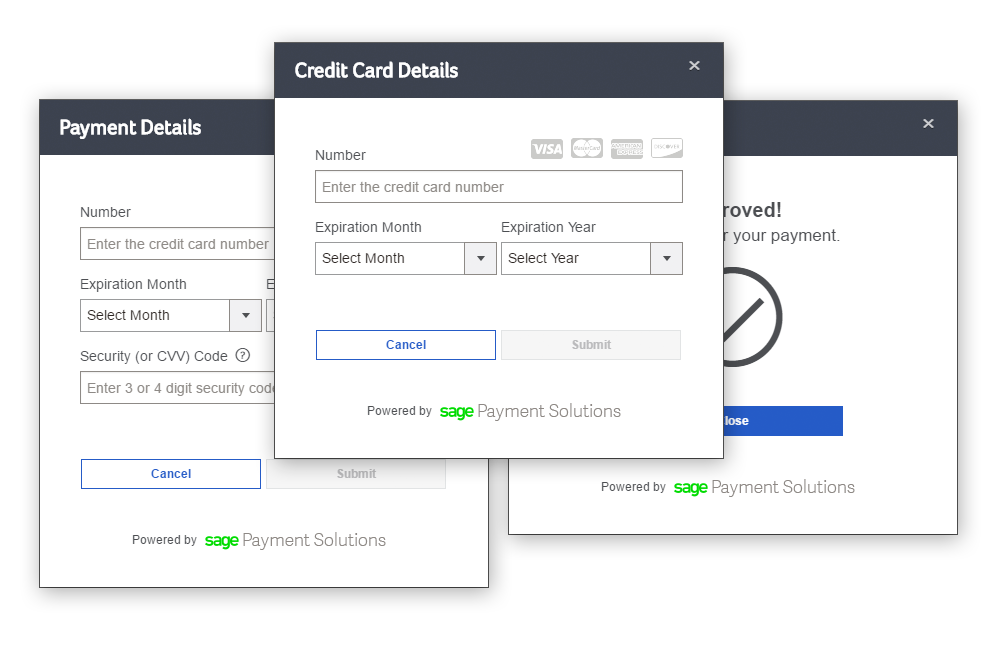
PaymentsJS is a JavaScript library that enables developers to quickly start processing credit cards on their website. The library includes a pre-built user interface, while also exposing the underlying methods for use in applications with more strict UI/UX requirements. And whichever route you go, the credit card data never touches your server.
Add the library:
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.sagepayments.net/pay/1.0.2/js/pay.min.js"></script>And a button:
<button id="paymentButton">Pay Now</button>Then initialize the UI:
<script type="text/javascript">
PayJS(['PayJS/UI'], // loading the UI module...
function($UI) { // ... and assigning it to a variable
$UI.Initialize({
elementId: "paymentButton",
// identifiers (no keys!):
clientId: "myClientId", // https://developer.sagepayments.com/user/register
merchantId: "999999999997",
// auth, covered later:
authKey: "ABCD==",
salt: "DEFG==",
// config:
requestType: "payment", // or "vault" to tokenize a card for later
amount: "1.00",
orderNumber: "Invoice12345",
// convenience:
addFakeData: true,
});
});
</script>Clicking on paymentButton will make the payment window appear. You can submit the transaction, but it won't succeed -- so our next step is to calculate the authKey.
Credit card data moves directly between the user's browser and Sage Payment Solutions' secure payment gateway. This is great news for your server, which doesn't have to touch any sensitive data; but, as with any client-side code, it means we have to be wary of malicious users.
The authKey is an encrypted version of the configuration settings that you pass into UI.Initialize() or CORE.Initialize(). We'll decrypt the authKey and compare it to the request body, to make sure that what we received matches what you were expecting. This is also how you send us your merchantKey, which should never be exposed to the client browser.
The follow code snippets show the encryption in PHP; check out the samples in this repository for other languages. If we don't have a sample in your language, the Developer Forums are a great resource for information and support.
First, we need a salt and an initialization vector:
$iv = openssl_random_pseudo_bytes(16);
$salt = base64_encode(bin2hex($iv));Next, we're going to create an array that contains our configuration settings, plus our merchantKey:
$req = [
"clientId" => "7SMmEF02WyC7H5TSdG1KssOQlwOOCagb",
"merchantId" => "999999999997",
"merchantKey" => "K3QD6YWyhfD",
"requestType" => "payment",
"orderNumber" => (string)time(),
"amount" => "1.00",
"salt" => $salt,
];We convert it to JSON...
$jsonReq = json_encode($req);... and then use our client key to encrypt it:
$clientKey = "wtC5Ns0jbtiNA8sP";
$passwordHash = hash_pbkdf2("sha1", $clientKey, $salt, 1500, 32, true);
$authKey = openssl_encrypt($jsonReq, "aes-256-cbc", $passwordHash, 0, $iv);Now that we have our authKey, we initialize the UI with the same values:
PayJS(['PayJS/UI'],
function($UI) {
$UI.Initialize({
clientId: "<?php echo $req['clientId'] ?>",
merchantId: "<?php echo $req['merchantId'] ?>",
requestType: "<?php echo $req['requestType'] ?>",
orderNumber: "<?php echo $req['orderNumber'] ?>",
amount: "<?php echo $req['amount'] ?>",
authKey: "<?php echo $authKey ?>",
salt: "<?php echo $salt ?>",
elementId: "paymentButton",
addFakeData: true
});
$UI.setCallback(function($RESP) { // fires after the payment
console.log($RESP.getResponse());
});
});The payment now goes through!
The following fields should always be included in the authKey encryption:
merchantIdmerchantKeyrequestTypeorderNumber(akarequestId)salt(akanonce)
These optional fields need to be included in the authKey only if they are used:
amounttaxAmountshippingAmountpreAuthpostbackUrltokendatadoVault
The response body that is returned to the client library (and, optionally, to the postbackUrl) includes the gateway response and the original requestId (orderNumber). If the request included custom data, this is also echoed in the response body:
{
"requestId":"Invoice12345",
"gatewayResponse":"{\"status\":\"Approved\",\"reference\":\"A12BCdeFG0\", ... }",
"data":"Some business-specific information.",
}The response headers contain a responseHash, which is a SHA-512 HMAC of the response body.
Use your client key to verify this hash on the server before shipping any orders, updating any databases, etc.
PaymentsJS uses RequireJS to manage its components. Your page will only load the modules that you specify (plus any unspecified dependencies).
The following modules contain methods that you may want to use in your project:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| "jquery" | Version 2.0 of the common JavaScript library. |
| "PayJS/Core" | Manages configuration settings and other shared values. |
| "PayJS/UI" | Configures and manages the user interface. |
| "PayJS/Request" | Sends transaction and vault requests to the gateway. |
| "PayJS/Response" | Reads information from gateway responses. |
| "PayJS/Formatting" | Converts credit card data into standardized strings. |
| "PayJS/Validation" | Checks credit card data for acceptable values. |
If you're already using RequireJS on your page, add a path to PaymentsJS --
requirejs.config({
paths: {
"PayJS": 'https://www.sagepayments.net/pay/1.0.2/js/build'
},
});
-- and then use it like you would any other module.
Please keep in mind that you'll also need to provide your own jQuery dependency if you don't already have one.
- Module Loading - PayJS()
- PayJS/Core
- PayJS/UI
- PayJS/Request
- PayJS/Response
- PayJS/Formatting
- PayJS/Validation
The entire PaymentsJS library is accessed through the PayJS function, which takes two arguments:
PayJS(
// first, a string array containing the names of the modules you want to use
['moduleOne', 'moduleTwo'],
// and second a function, inside which you can use those modules
function(m1, m2){ // moduleOne is assigned to m1, moduleTwo to m2
m1.doSomething();
m2.doSomethingElse();
}
);Or, less generically:
PayJS(['PayJS/Core', 'PayJS/Request'],
function(CORE, REQ){
CORE.Initialize(/*...*/);
REQ.doPayment(/*...*/);
});The Core module's main role is to share common settings among the other modules.
Configures the library for a gateway request. If you're running payments using the PayJS/Request module, use this instead of UI.Initialize().
This method takes a single argument:
// pass this method an object literal containing your configuration settings
CORE.Initialize({
someValue: "123456",
mySetting: true
});The configuration object can contain:
| Name | Description | Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| clientId | your developer id | alphanumeric string | yes |
| merchantId | identifies your gateway account | numeric 12-character string | yes |
| authKey | see Authentication & Verification | base64 string | yes |
| salt | the encryption salt; see Authentication & Verification | base64 string | yes |
| orderNumber | an identifier of your choosing | string | yes |
| requestType | chooses between charging or tokenizing a card | "payment" or "vault" | yes |
| amount | the total amount to charge the card | "1.00", etc. | when requestType == "payment" |
| taxAmount | the amount charged as tax | "1.00", etc. | no |
| shippingAmount | the amount charged for shipping | "1.00", etc. | no |
| preAuth | toggles between authorization-only (true) and authorization & capture (false) | boolean | no, default false |
| allowAmex | causes VALIDATION.isValidCreditCard() to return false if it is passed an American Express card; when using the UI module, this also prevents submission |
boolean | no, default true |
| allowDiscover | behaves like allowAmex, but for Discover | boolean | no, default true |
| postbackUrl | a URL that will receive a copy of the gateway response | valid URI with https scheme | no |
| billing | add billing information (address/etc.) to the transaction request | see CORE.setBilling() |
no |
| shipping | add shipping information (address/etc.) to the transaction request | see CORE.setShipping() |
no |
| customer | add customer contact information (email/phone) to the transaction request | see CORE.setCustomer() |
no |
| level2 | add level2 data to the transaction request | see CORE.setLevel2() |
no |
| level3 | add level3 to the transaction request | see CORE.setLevel3() |
no |
| isRecurring | indicate that a payment should also create a recurring transaction | boolean | no, default false |
| recurringSchedule | add customer contact information (email/phone) to the transaction request | see CORE.setRecurringSchedule() |
when isRecurring == true |
| debug | enable verbose logging to browser console | boolean | no, default false |
| environment | choose between the certification and production environments | "cert" or "prod" | no, default "cert" |
| data | add custom data that is echoed in the response | string | no |
| token | the vault token being passed to REQUEST.doTokenPayment() |
alphanumeric string | when running a token payment |
| doVault | when processing a payment, also tokenize the card | boolean | no, default false |
Returns a boolean that represents whether the module has been successfully initialized.
This method does not take any arguments:
CORE.isInitialized();
// => false
CORE.Initialize(validSettings)
CORE.isInitialized();
// => trueAdds billing information to a payment request.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setBilling({
name: "John Smith",
address: "123 Address St",
city: "Denver",
state: "CO",
postalCode: "12345",
country: "USA"
});Notes:
- Billing information can also be set during initialization.
Adds shipping information to a payment request.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setShipping({
name: "John Smith",
address: "123 Address St",
city: "Denver",
state: "CO",
postalCode: "12345",
country: "USA"
});Notes:
- Shipping information can also be set during initialization.
Adds customer information to a payment request.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setCustomer({
email: "[email protected]",
telephone: "7035551234",
fax: "8041239999"
});Notes:
- Customer information can also be set during initialization.
Adds Level II data to a payment request.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setLevel2({
customerNumber: "123456789"
});Notes:
- Level II data can also be set during initialization.
Adds Level III data to a payment request.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setLevel3({
destinationCountryCode: "840",
amounts: {
discount: 1,
duty: 1,
nationalTax: 1
},
vat: {
idNumber: "123456789",
invoiceNumber: "Invoice12345",
amount: 1,
rate: 1
},
customerNumber: "123456789"
});Notes:
- Level III data can also be set during initialization.
- Level III processing requires additional API calls.
Indicates that a payment should also create a recurring transaction that processes automatically on a defined schedule.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setIsRecurring(true);Notes:
- When setting this to true, don't forget to define the recurring schedule.
Defines the processing schedule for a recurring transaction.
This method takes a single argument:
CORE.setRecurringSchedule({
"amount": 100,
"interval": 3,
"frequency": "Monthly",
"totalCount": 4,
"nonBusinessDaysHandling": "After",
"startDate": "2016-10-21T21:06:44.385Z",
"groupId": "123456"
});Notes:
- When defining a recurring schedule, don't forget to set the isRecurring flag.
These methods return information about the module state:
// auth:
CORE.getClientId()
CORE.getAuthKey()
CORE.getSalt()
// merchant:
CORE.getMerchantId()
CORE.getPhoneNumber()
// environments/targets:
CORE.getApiUrl()
CORE.getClientUrl()
CORE.getEnvironment()
CORE.getPostbackUrl()
CORE.getLanguage()
// gateway:
CORE.getOrderNumber()
CORE.getRequestType()
CORE.getDoVault()
// transaction:
CORE.getPreAuth()
CORE.getAmount()
CORE.getTaxAmount()
CORE.getShippingAmount()
CORE.getLevel2()
CORE.getLevel3()
CORE.getIsRecurring()
CORE.getRecurringSchedule()
// customer/cardholder:
CORE.getBilling()
CORE.getCustomer()
CORE.getShipping()
// backwards-compatibility:
CORE.getRequestId() // getOrderNumber()
CORE.getApiKey() // getClientId()
CORE.getNonce() // getSalt()
// misc/other:
CORE.getCustomData()The UI module adds a pre-built payment form to your website.
Configures the library for a gateway request. If you're using the pre-built payment form, use this instead of CORE.Initialize().
This method takes a single argument:
// pass this method an object literal containing your configuration settings
UI.Initialize({
someValue: "123456",
mySetting: true
});In addition to the information outlined in CORE.Initialize(), this configuration object can contain:
| Name | Description | Values | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| elementId | the id of the html element to which the UI will attach | string | yes |
| suppressResultPage | hide the approved/declined pages that show after a gateway request | boolean | no, default false |
| restrictInput | limits user entry to acceptable characters | boolean | no, default true |
| formatting | after the user enters their credit card number, the form will remove invalid characters and add dashes | boolean | no, default true |
| phoneNumber | displayed as a support number for declined transactions | string | no |
| show | automatically show the modal UI when ready | boolean | no, default false |
| addFakeData | adds fake credit card data to the form, for testing | boolean | no, default false |
Notes:
- If
targetElementrefers to a<button>,<a>, or<input>, the UI will appear as a modal dialog when that element is clicked. If it refers to a<div>, the UI will be put inside the element. - If
suppressResultPageis enabled, the UI will never move past the processing bar. This can be used in conjunction withUI.setCallback()to customize response handling (eg, redirecting to another page). - We do not recommend changing
restrictInputorformattingtofalse. (These options may be deprecated in a future release.)
Returns a boolean that represents whether the module has been successfully initialized.
This method does not take any arguments:
UI.isInitialized();
// => false
UI.Initialize(validSettings)
UI.isInitialized();
// => trueSets a function that executes after a request completes.
This method takes up to four arguments:
var myCallback = function(RESP, data|jqXHR, textStatus, jqXHR|errorThrown){
SendResultToServer(RESP.getResponse({ json: true }))
var wasApproved = RESP.getTransactionSuccess();
RedirectUser(wasApproved ? "approved.html" : "declined.html");
};
UI.setCallback(myCallback);Notes:
- The first argument to your callback function is the
PayJS/Responsemodule.- You do not need to call
RESPONSE.tryParse()yourself.
- You do not need to call
- The final three arguments are passed through from jQuery's ajax method; please refer to the jQuery documentation for more information.
- Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
The Request module sends transaction and vault requests to the payment gateway.
Charges a credit card.
This method takes four arguments:
REQUEST.doPayment(cardNumber, expirationDate, cvv, callbackFunction);Notes:
- The arguments to your callback are passed through from jQuery's ajax method; please refer to the jQuery documentation for more information.
- Pass the response string into
RESPONSE.tryParse()to initialize thePayJS/Responsemodule's getters.
- Pass the response string into
- Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
Tokenizes a credit card without charging it. The token can be used later to charge the card.
This method takes three arguments (CVVs can not be stored):
REQUEST.doVault(cardNumber, expirationDate, callbackFunction);Notes:
- The arguments to your callback are passed through from jQuery's ajax method; please refer to the jQuery documentation for more information.
- Pass the response string into
RESPONSE.tryParse()to initialize thePayJS/Responsemodule's getters.
- Pass the response string into
- Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
Charges a credit card using a vault token.
This method takes three arguments:
REQUEST.doTokenPayment(token, cvv, callbackFunction);Notes:
- The
tokenmust be specified in the authKey. - An empty string is an acceptable CVV value; however, to maximize the chances of the cardholder's bank approving the transaction, it is always preferable to collect and include a CVV whenever possible.
- The arguments to your callback are passed through from jQuery's ajax method; please refer to the jQuery documentation for more information.
- Pass the response string into
RESPONSE.tryParse()to initialize thePayJS/Responsemodule's getters.
- Pass the response string into
- Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
Get payment details for the last credit card charged or stored through PaymentsJS.
This method does not take any arguments:
REQUEST.doPayment("5424180279791732", "1017", "123", function() {
console.log( REQUEST.getLastCard() );
// => Object {maskedNumber: "XXXXXXXXXXXX1732", cardType: "5", BIN: "542418", lastFourDigits: "1732", expirationDate: "1017"}
});Notes:
- For convenience, this method has the alias
RESPONSE.getPaymentDetails(). - The BIN identifies the bank that issued the card. For more, please see this article.
- The card type is represented by the first digit of that card type.
3-- American Express4-- Visa5-- MasterCard6-- Discover
The Response module exposes methods for traversing transaction results.
Attempts to initialize this module's getters from an AJAX response.
This method takes up to three arguments:
RESPONSE.tryParse(data|jqXHR, textStatus, jqXHR|errorThrown);
// => trueNotes:
- The arguments are passed through from jQuery's ajax method; please refer to the jQuery documentation for more information.
- This method is used in the callback functions of the
PayJS/Requestmodule's methods.- Use
RESPONSE.tryParse()to initialize thePayJS/Responsemodule's getters. - You do not need to use this method in
UI.setCallback().
- Use
These methods return different layers of the data:
They do not take any arguments:
// returns the jqXHR object returned by the AJAX request:
RESPONSE.getAjaxResponse();
// => Object {
// readyState: 4,
// responseText: "{"requestId":"Invoice12345","gatewayResponse":{"status":"Approved", "orderNumber":"Invoice12345", (...)
// (...)
// }
// returns the json string that the library received from the proxy api:
RESPONSE.getApiResponse();
// => "{"requestId":"Invoice12345","gatewayResponse":{"status":"Approved", "orderNumber":"Invoice12345", (...)
// returns the deserialized inner response from the payment gateway:
RESPONSE.getGatewayResponse();
// => Object {
// status: "Approved",
// orderNumber: "Invoice12345",
// (...)
// }Notes:
- When using the
PayJS/Requestmodule's methods, you must callRESPONSE.tryParse()before these methods are available. ThePayJS/UImodule does this for you. - Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
Returns the API response and its hash. Send these values server-side for hash verification.
This method does not take any arguments:
RESPONSE.getResponseHash();
// => Object {
// response: "{"requestId":"Invoice12345","gatewayResponse":{"status":"Approved", "orderNumber":"Invoice12345", (...)",
// hash: "ABCD==",
// }Notes:
- Always check the response hash server-side to verify the integrity of the response.
This module has various getters that return information about the gateway request.
These methods do not take any arguments:
// returns true if the payment request was approved; otherwise, false
RESPONSE.getTransactionSuccess();
// => true
// returns true if the vault request was approved; otherwise, false
RESPONSE.getVaultSuccess();
// => true
// returns the token representing the credit card in the vault
RESPONSE.getVaultToken();
// => "d01a3475-42ad-4d7e-b0a6-76e4ea1abec6"
// returns the approval or decline code
RESPONSE.getCode();
// => "123456"
// returns the approval or decline message
RESPONSE.getMessage();
// => "APPROVED"
// returns the unique gateway identifier for the payment
RESPONSE.getReference();
// => "123456789123"
// returns the payment's order number
RESPONSE.getOrderNumber();
// => "123456789123"
// returns information about the credit card
RESPONSE.getPaymentDetails();
// => Object {maskedNumber: "XXXXXXXXXXXX1732", cardType: "5", BIN: "542418", lastFourDigits: "1732", expirationDate: "1017"}These methods can take a configuration object as a single optional argument:
// without any configuration, this method returns a single character representing the result of an AVS check
// (see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_Verification_System)
RESPONSE.getAVS();
// => "Z"
// use the "require" option to test whether the actual AVS result meets a certain level (or higher)
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "none" }); // no match
// => true
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "partial" }); // partial match (address OR zip)
// => true
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "exact" }); // exact match (address AND zip)
// => false
// use the "require" option with the "test" option to test the given code for a certain match-level, irrespective of the actual AVS result
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "none", test: "M" });
// => true
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "partial", test: "M" });
// => true
RESPONSE.getAVS({ require: "exact", test: "M" });
// => true// without any configuration, this method returns a single character representing the result of a CVV check
RESPONSE.getCVV();
// => "M"
// use the "require" option to determine whether it was a match or not
RESPONSE.getCVV({ require: "match" }); // no match
// => trueThe Formatting module converts strings into default or specified formats.
Converts a string into a formatted credit card number.
This method can take one or two arguments:
// pass the string to format
FORMATTING.formatCardNumberInput("5454545454545454");
// => "5454-5454-5454-5454"
FORMATTING.formatCardNumberInput("371449635392376");
// => "3714-496353-92376"
// pass a delimiter to use instead of a dash
FORMATTING.formatCardNumberInput("4111111111111111", "$");
// => "4111$1111$1111$1111"
// non-numeric characters are removed:
FORMATTING.formatCardNumberInput("4111-1111_1111a1111", "");
// => "4111111111111111"Converts a string into a formatted expiration date.
This method can take one or two arguments:
// pass the string to format
FORMATTING.formatExpirationDateInput("1216");
// => "12/16"
// pass a delimiter to use instead of a slash
FORMATTING.formatExpirationDateInput("1216", "~");
// => "12~16"Notes:
- See
VALIDATION.getExpArray()for more on expiration date string parsing.
Masks a credit card number, so that only the last four digits are visible.
This method requires a single argument:
FORMATTING.maskCreditCardNumber("5454545454545454");
// => "XXXXXXXXXXXX5454"
FORMATTING.maskCreditCardNumber("371449635392376");
// => "XXXXXXXXXXX2376"Optionally, pass a configuration object:
// include the first six digits (BIN/IIN)
FORMATTING.maskCreditCardNumber("5454545454545454", { showBin: true });
// => "545454XXXXXX5454"
// use something other than 'X'
FORMATTING.maskCreditCardNumber("5454545454545454", { maskChar: '$' });
// => "$$$$$$$$$$$$5454"Removes from a string any characters other than digits.
This method takes a single argument:
FORMATTING.stripNonNumeric("abcd1234!@#$");
// => "1234"Removes from a string any characters other than digits, letters, and underscores.
This method takes a single argument:
FORMATTING.stripNonAlphanumeric("abcd1234!@#$");
// => "abcd1234"The Validation module tests that strings meet certain validity criteria.
Tests a credit card string for invalid characters, appropriate length, and mod10.
This method can take one or two arguments:
// pass the string to validate
VALIDATION.isValidCreditCard("5454545454545454");
// => true
// pass a card type to check validity for that particular type
VALIDATION.isValidCreditCard("5454545454545454", "3");
// => falseNotes:
- This method will allow dashes; all other non-numeric characters will result in
false. - This method expects American Express cards to have 15-digit cardnumbers; all other cardnumbers are expected to be 16 digits.
- The card type is represented by the first digit of that card type.
3-- American Express4-- Visa5-- MasterCard6-- Discover
Tests an expiration date string for invalid characters, impossible month, or past date.
This method takes a single argument:
VALIDATION.isValidExpirationDate("1220");
// => true
// expired
VALIDATION.isValidExpirationDate("1215");
// => false
// impossible date
VALIDATION.isValidExpirationDate("1320");
// => falseNotes:
- This method will allow slashes; all other non-numeric characters will result in
false. - See
VALIDATION.getExpArray()for more on expiration date string parsing.
Tests a CVV string for invalid characters and appropriate length.
This method takes two arguments:
// pass the string to validate, and a card type to check validity for that particular type
VALIDATION.isValidCvv("123", "4");
// => true
VALIDATION.isValidCvv("1234", "4");
// => false
VALIDATION.isValidCvv("1234", "3");
// => trueNotes:
- This method expects American Express cards to have 4-digit CVVs ("CIDs"); all other CVVs are expected to be 3 digits.
- The card type is represented by the first digit of that card type.
3-- American Express4-- Visa5-- MasterCard6-- Discover
Returns a string array containing an expiration date as ["MM", "YY"].
This method takes a single argument:
// with a slash
VALIDATION.getExpArray("01/18"); // MM/YY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("1/18"); // M/YY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("01/2018"); // MM/YYYY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("1/2018"); // M/YYYY
// => ["01", "18"];
// without a slash
VALIDATION.getExpArray("0118"); // MMYY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("118"); // MYY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("012018"); // MMYYYY
// => ["01", "18"];
VALIDATION.getExpArray("12018"); // MYYYY
// => ["01", "18"];Notes:
- Despite its parent module, this method does not validate the string.
VALIDATION.isValidExpirationDate()calls this method before validating.
ENHANCEMENTS:
- The API now returns a single response hash in the header.
- All callback functions now receive all of jQuery's ajax/jqXHR arguments.
- The RESPONSE module has four new methods:
getAjaxResponse: returns the AJAX response objectgetApiResponse: returns the API response stringgetGatewayResponse: returns the inner gateway response, deserializedgetResponseHash: returns an object with the API response and its hash -Documentation and Samples have been updated accordingly.
BUG FIXES:
- User is no longer able to hide the modal dialog while a request is pending.
- Better support for overflow when the modal dialog is open on small, landscape screens.
- Explicated certain CSS rules to avoid being overriden by parent styles; redundant in most cases.
- The response sent to the postbackUrl now includes a Content-Type header.
- The vault token is no longer an exception to authKey validation.
- The response data now echoes the requestId/orderNumber, with a hash.
ENHANCEMENTS:
- User can now set allowAmex and allowDiscover.
- The library can now be initialized with a 'data' field.
- This field is echoed back in the response, with a hash.
- New method: FORMATTING.maskCreditCardNumber().
- New method: REQUEST.getLastCard().
- This method also exists under the alias RESPONSE.getPaymentDetails().
MISC/OTHER:
- Changes to JSON de/serialization.
- The API now returns the gateway response as a string, rather than an object.
- The ajax requests in the REQUEST module now return JSON strings, rather than an object.
- RESPONSE.tryParse() has been adjusted to expect a JSON string.
- RESPONSE.getResponse() returns a completely-deserialized object, as before.
- RESPONSE.getResponse() no longer has a json option.
- RESPONSE.getRawResponse() now returns the original AJAX response, before any de/serialization.
- API requests now include a version header.
- Pre-patch for Kount integration.
- Payments no longer automatically vault the card.
- This functionality is now available via a 'doVault' option.
BUG FIXES:
- Billing data no longer required.
- (Note: transactions processed without address data may incur additional fees.)
- Server now includes appropriate Cache-Control headers.
- "no-store" for contents of /js, "no-cache" for /css and /img
- UI now updates card type when using addFakeData option.
- When authKey decryption fails, server response now includes CORS headers.
- When authKey validation fails, server response now includes CORS headers.
- When authKey validation fails, server response now 401 instead of 400.
- When authKey validation fails, server response now specifies failures.
- When preAuth defaults (or is set) to false, it is ignored during authKey validation.
- When postbackUrl is not provided, it is ignored during authKey validation.
ENHANCEMENTS:
- Developer can now set customer data.
- Developer can now set shipping data.
- Developer can now set level2 data.
- Developer can now set level3 data.
- Developer can now set taxAmount.
- Developer can now set shippingAmount.
- Developer can now set isRecurring + recurringSchedule.
- Token payments now pass CVV.
MISC/OTHER:
- The 'requestId' is now named 'orderNumber'.
- The 'apiKey' is now named 'clientId'.
- The 'nonce' is now named 'salt'.
- (Note: renamed fields retain their old aliases and getters/setters, for backwards compatibility.)
- UI text abstracted out to separate module.
- Added a language option; value currently hard-coded to "en".
- UI.Initialize() is now more closely aligned to CORE.Initialize() in terms of return values and exceptions.
- Added this changelog to the GitHub readme.
- Created changelog.
- Added a build version.
- Fixed bug where PaymentsJS failed to pass address and zip to the gateway.
- UI module no longer forces billing data into an incorrect format.
- Initial Release