███████ ██ ██ ░██░░░░██ ░██ ░██ █████ ░██ ░██ █████ ░██ ░██ ██████ ██░░░██ ░██ ░██ ██░░░██░██████ ░██ ██░░░░██░██ ░██ ░██ ░██░███████░██░░░██ ░██░██ ░██░░██████ ░██ ██ ░██░░░░ ░██ ░██ ░██░██ ░██ ░░░░░██ ░███████ ░░██████░██████ ███░░██████ █████
There is no I in team, but there is an U in fun.
Log debug information from vim-scripts and commandline to file. Typically to use in combination with tail.
- Show execution time from last entry
- Accumulated execution time (Not excluding the rather heavy overhead from deblog)
- File
- Absolute linenumber of call
- Calling function (if any)
- Can dump objects
-
source or add the
deblog.vimfile in a directory where it is sourced at startup -
In target script: add
commands by calling boot in a script of your choosing:
for c in g:Deblog2.boot() | exe c | endforNB! Due to scopes this has to be done in the file you want to access/log local script variables. This goes fro the commands, calls can be done with local script variables from any file, but wil not include file, linenumber etc.
Globals, strings etc. can be logged form anywhere.
This adds the following commands that can be used in script for easy and clean logging:
| Command | Description / Examples |
|---|---|
| DUMP | Dump anything |
DUMP "Some objects: ", s:my_obja, s:other_obj DUMP s:foo |
|
| LLOG LLOG2 LLOG3 LLOG4 |
Log with file:line and call information each command can be silenced one can turn logging on / off for selected information. |
LLOG "The ID=" . string(s:foo.id) |
|
| LOG | Plain logging. Does not log filename, linenumber, function, ... |
LOG "Hello" |
|
| QLOG | Quoted plain logging. Same as LOG but output is wrapped in quotes. |
QLOG "Hello" |
|
| EXLOG | Log result of executing |
EXLOG reltime()EXLOG :messagesEXLOG :verbose function |
|
| DEBLOGSHELLTAIL | Open pre-defined shell with tail N -f log-file (read here) |
| DEBMUTE | Mute output: do not write to log file. Note that the deblog script functions are still called. To prevent calling one have to call g:Deblog2.mute(), but this result in loss of environment if un-muting from different script. See Using calls |
| DEBUNMUTE | Un-mute output: write to log file |
The various functions can also be called by :call g:Deblog2. ...., look at the source and / or the Using calls section. Notable functions:
In script one want to log
" Load all log commands
for c in g:Deblog2.boot() | exe c | endfor
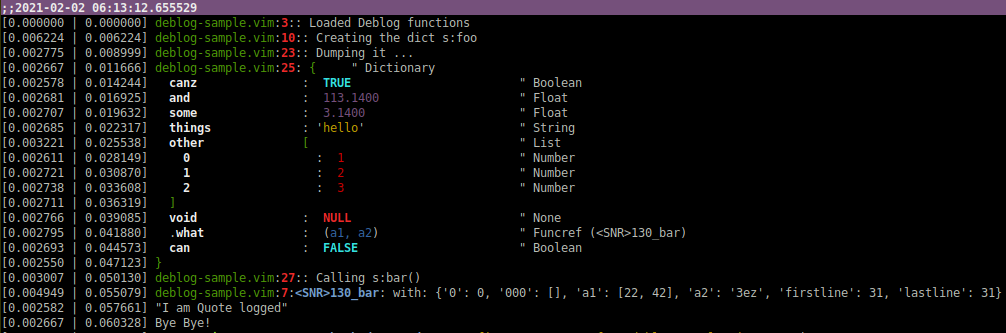
LLOG "Loaded Deblog functions"
fun! s:bar(a1, a2)
" log arguments
LLOG "with: " . string(a:)
endfun
LLOG "Creating the dict s:foo"
" A sample dict
let s:foo = {
\ 'some': 3.14,
\ 'things': "hello",
\ 'and': 113.14,
\ 'can': v:false,
\ 'canz': v:true,
\ 'other': [1, 2, 3],
\ 'what': function('s:bar'),
\ 'void': v:null,
\ }
LLOG "Dumping it ..."
" Dump the object s:foo
DUMP s:foo
LLOG "Calling s:bar()"
" Call function which is logging
call s:bar([22, 42], '3ez')
QLOG "I am Quote logged"
call g:Deblog2.spew('Bye Bye!')
Result:
- Column one show time passed since last log entry.
- Column two show the time accumulated since last time reset (header). The time resets if there is more then
htimeseconds since last call to print. Defaults to 0.5sec if Vim has reltime, else 1sec.
If you want to log local script variables etc. by command, the "Load all log commands" have to be done in that script file!
The commands can also be executed from commandline, e.g:
:DUMP s:
will dump the script environment from where the commands was defined.
Typically do tail -f log_file. Log file defaults to $HOME/.vim/my_deblog.log
Optionally do :DEBLOGSHELLTAIL from vim to open a predefined shell.
Look at s:shells for specifications.
Selected shell is set at load time to g:Deblog.cmd_shell and defaults to uxterm. Modify to meet your needs.
Ampersand is added on execution.
The placeholders #FILE# and #NTAIL# are replaced with the name of the log-file and number of potentionally existing lines to show on start:
'uxterm -geometry 85x90-0+0 -T "Deblog #FILE#" -e "tail #NTAIL# -f #FILE#"'With ntail set to 20 and file set to /home/foo/.vim/my_deblog.log result in:
'uxterm -geometry 85x90-0+0 -T "Deblog /home/foo/.vim/my_deblog.log" -e "tail 20 -f /home/foo/.vim/my_deblog.log" &'Other commands:
DEBMUTE: Stop writing to log fileDEBUNMUTE: Resume logging
The g:Deblog.boot([COMMANDS]) function return a list of pre-defined command definitions that can be executed.
Optionally one can add a list as an argument with selected commands one want to get. E.g. ["LLOG", "DUMP"] will only return the commands for those.
If noone given all will be returned.
boot() always defines DEBLOGSHELLTAIL, DEBMUTE and DEBUNMUTE. These are not returned in the call.
-
g:Deblog2.spew(str msg || [str msg, str msg, ...])– write to logfile without using command -
g:Deblog2.objdump(str title, obj object)– dump object -
g:Deblog2.evex(str expression)– Executeexpressionand log result. -
g:Deblog2.shell([int ntail])– Open shell with tail.ntailis number of lines to include at start. -
g:Deblog2.wipe()– Try to remove deblog from environment. -
g:Deblog2.mute([COMMANS])– Redirect calls to commands to a Nop function. Optionally a list of commands can be given as argument. -
g:Deblog2.unmute([COMMANDS])– Returns a list of commands that can be executed to re-enable muted commands. NB! The environment from which they are executed wil become the environment where commands can read script variables. -
g:Deblog2.cmute()– A soft mute. Calls will go trough, but nothing written to log file. -
g:Deblog2.cunmute()– Re-enable writing to log file.
If one want to log local script variables from multiple source files one way is to do:
call g:Deblog2.objdump("foo2", s:foo2)and the like.
This will not include script file or line numbers etc. You could add a separate, local command for each script file and call cmd_call().
Hack away.