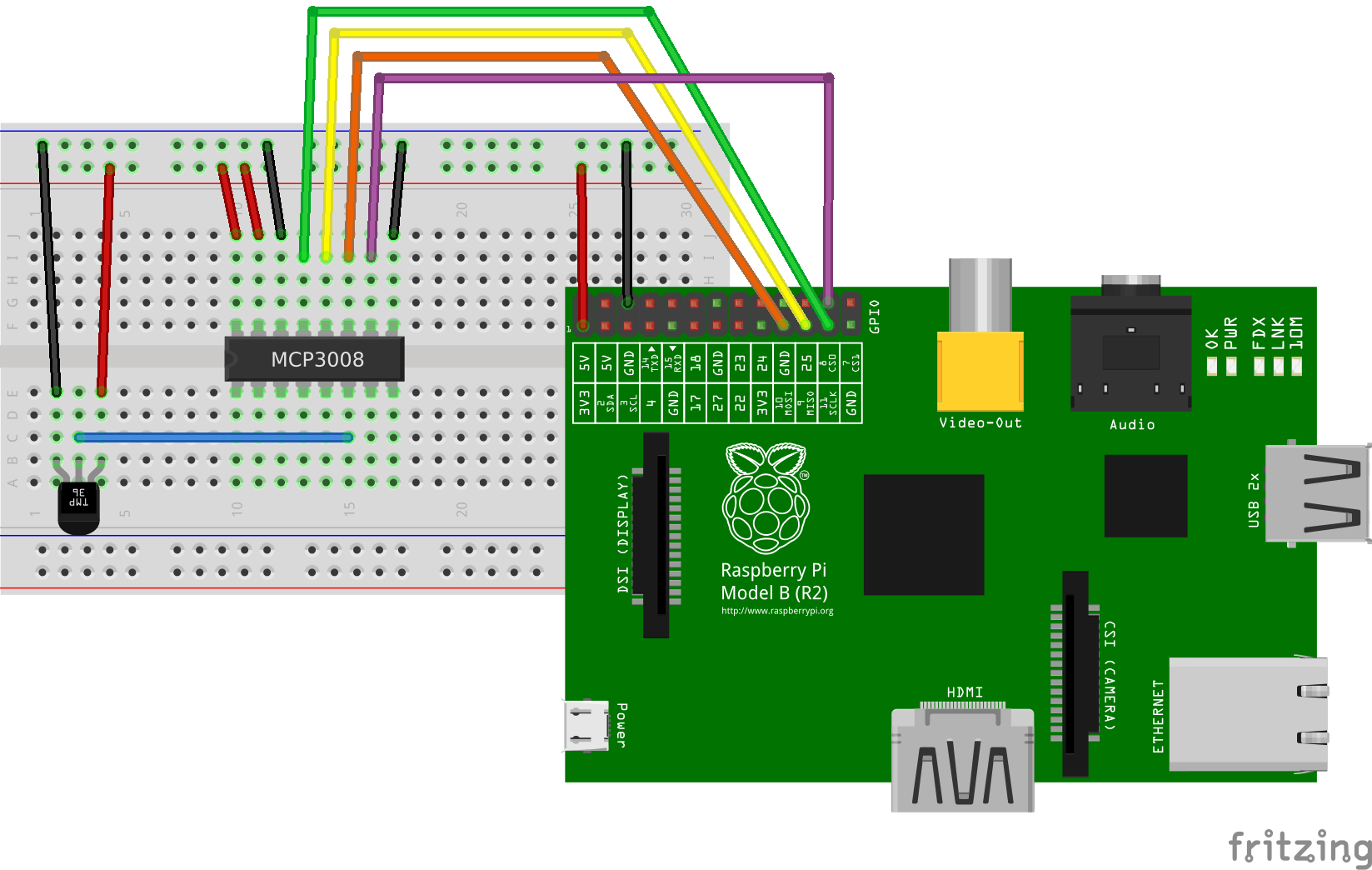
MCP3002/4/8, MCP3202/4/8 and MCP3304 SPI analog to digital conversion with Node.js on Linux boards like the Raspberry Pi Zero, 1, 2, or 3 or BeagleBone Black.
mcp-spi-adc supports Node.js versions 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12.
npm install mcp-spi-adc
In order to use mcp-spi-adc SPI must be enabled. How SPI is enabled varies from board to board. For example, on the Raspberry Pi the raspi-config tool can be used enable SPI. On the BeagleBone Black the config-pin utility can be used.
Determine the temperature using a TMP36 analog temperature sensor wired to channel 5 on an MCP3008 SPI A/D converter.
const mcpadc = require('mcp-spi-adc');
const tempSensor = mcpadc.open(5, {speedHz: 20000}, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
setInterval(() => {
tempSensor.read((err, reading) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log((reading.value * 3.3 - 0.5) * 100);
});
}, 1000);
});Note how the optional configuration option speedHz is used to configure the SPI clock frequency in Hertz for reading the value from the TMP36 temperature sensor. The default SPI clock frequency for the MCP3008 is 1350000Hz but lowering it to 20000Hz gives a more acurate temperature reading. In general, it's not necessary to lower the clock speed to read a value.
The default clock speed of 1350000Hz for the MCP3008 is derived from the MCP3008 datasheet. The maximum sampling rate at VDD = 2.7V is 75 ksps and each sample requires an 18-bit transfer. 75000 x 18 = 1350000. 1350000Hz is a conservative frequency in the above circuit as VDD is 3.3V.
| Device | Channels | Channel Numbers | Default Clock Frequency | Resolution | Raw Value Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCP3002 | 2 | 0-1 | 1200000Hz | 10-bit | 0-1023 |
| MCP3004 | 4 | 0-3 | 1350000Hz | 10-bit | 0-1023 |
| MCP3008 | 8 | 0-7 | 1350000Hz | 10-bit | 0-1023 |
| MCP3202 | 2 | 0-1 | 900000Hz | 12-bit | 0-4095 |
| MCP3204 | 4 | 0-3 | 1000000Hz | 12-bit | 0-4095 |
| MCP3208 | 8 | 0-7 | 1000000Hz | 12-bit | 0-4095 |
| MCP3304 | 8 | 0-7 | 1050000Hz | 13-bit | 0-4095 |
All methods are asynchronous and take a completion callback as their last argument. The arguments passed to the completion callback depend on the method, but the first argument is always reserved for an exception. If the operation was completed successfully, then the first argument will be null or undefined.
- openMcp3002(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3004(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3008(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3202(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3204(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3208(channel[, options], cb)
- openMcp3304(channel[, options], cb)
- open(channel[, options], cb) - alias for openMcp3008(channel[, options], cb)
- channel - the number of the channel to open, see channel numbers in supported devices
- options - an optional object specifying channel configuration options
- cb - completion callback
Asynchronous open. Returns a new AdcChannel object. The completion callback gets one argument (err). The AdcChannel object returned should not be used before the completion callback is called.
The following channel configuration options are supported:
- busNumber - the SPI bus number, 0 for
/dev/spidev0.n, 1 for/dev/spidev1.n, ..., default 0 - deviceNumber - the SPI device number, 0 for
/dev/spidevn.0, 1 for/dev/spidevn.1, ..., default 0 - speedHz - a number representing the SPI clock frequency for reading from the channel in Hertz, see default clock frequency in supported devices
- cb - completion callback
Asynchronous read. The completion callback gets two arguments (err, reading). The reading argument is an object with the following properties:
- value - the value read from the channel scaled to a value between 0 and 1
- rawValue - the value read from the channel, see raw value range in supported devices
Returns this.
- cb - completion callback
Asynchronous close. The completion callback gets one argument (err). Returns null.