A Benchmark for Machine-Learning based Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Estimation using Photoplethysmogram
Sergio González, Wan-Ting Hsieh, and Trista Pei-Chun Chen
Blood Pressure (BP) is an important cardiovascular health indicator. BP is usually monitored noninvasively with a cuff-based device, which can be bulky and inconvenient. Thus, continuous and portable BP monitoring devices, such as those based on a photoplethysmography (PPG) waveform, are desirable. In particular, Machine Learning (ML) based BP estimation approaches have gained considerable attention as they have the potential to estimate intermittent or continuous BP with only a single PPG measurement. Over the last few years, many ML-based BP estimation approaches have been proposed with no agreement on their modeling methodology. To ease the model comparison, we designed a benchmark with four open datasets with shared preprocessing, the right validation strategy avoiding information shift and leak, and standard evaluation metrics. We also adapted Mean Absolute Scaled Error (MASE) to improve the interpretability of model evaluation, especially across different BP datasets. The proposed benchmark comes with open datasets and codes. We showcase its effectiveness by comparing 11 ML-based approaches of three different categories.
Paper (Nature Scientific Data): https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02020-6
Datasets (Figshare): https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.c.6150390.v1
#-- Create folder at your home or preferable directory
cd ~
mkdir bp_benchmark
cd bp_benchmark
#-- Download data (also check Datasets section)
mkdir -p ./datasets/splitted
cd ./datasets/splitted
# download the datasets from Figshare into ./datasets/splitted
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671832
unzip data.zip
# UCI
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671886
unzip data.zip
# BCG
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671817
unzip data.zip
# PPGBP
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671826
unzip data.zip
#-- Download trained models (download the models from Figshare into ./models/)
cd ../..
wget -O models.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671889
unzip models.zip
rm -r models.zip
#-- or Create the folder to save new models
mkdir ./models
cd ./models
#-- Clone project
cd ~/bp_benchmark # back to /bp_benchmark
git clone https://github.com/inventec-ai-center/bp-benchmark.git
cd bp-benchmark
#-- Build docker image
docker build -t bpimage .
docker run --gpus=all --shm-size=65g --name=bp_bm -p 9180-9185:9180-9185 -it -v ~/bp_benchmark/bp-benchmark/:/bp_benchmark -v ~/bp_benchmark/datasets/:/bp_benchmark/datasets -v ~/bp_benchmark/models/:/bp_benchmark/models bpimage bash
#-- Quick test the environment
cd code/train
python train.py --config_file core/config/ml/lgb/lgb_bcg_SP.yamlBefore running the training pipeline, the user could directly download the preprocessed datasets (recommended), or download raw datasets and process them.
The preprocessed datasets might be found in Figshare. They should be located under the directory /bp_benchmark/datasets/splitted/ to proceed with the training stage.
mkdir /bp_benchmark/datasets/splitted/
cd /bp_benchmark/datasets/splitted/
# Download the dataset under /bp_benchmark/datasets/splitted/
wget -O data.zip <link-to-figshare>
# Unzip the data
unzip data.zip
# OPTIONAL: remove unnecessary files
rm -r data.zip
# EXAMPLES:
# sensor
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671832
unzip data.zip
# UCI
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671886
unzip data.zip
# BCG
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671817
unzip data.zip
# PPGBP
wget -O data.zip https://springernature.figshare.com/ndownloader/files/38671826
unzip data.zip
The raw datasets should be located under the directory /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/ to proceed with the processing stage.
- sensors dataset might be found in Zenodo's website:
mkdir /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/sensors
cd /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/sensors
# Download sensors dataset under datasets/raw/sensors
wget https://zenodo.org/record/4598938/files/ABP_PPG.zip
# Unzip the data
unzip ABP_PPG.zip
# move files to desired path
mv ABP_PPG/* .
# OPTIONAL: remove unnecessary files
rm -r ABP_PPG ABP_PPG.zip 'completed (copy).mat' completed.mat - UCI dataset might be downloaded from UCI repository.
mkdir /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/UCI
cd /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/UCI
# Download UCI dataset under datasets/raw/UCI
wget https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00340/data.zip
# Unzip the data
unzip data.zip
- BCG dataset has to be downloaded manually from IEEEDataPort's site with an IEEE account.
mkdir /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/BCG
cd /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/BCG
# > Manually download the data from IEEEDataPort and
# > Locate 'Data Files.zip' under /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/BCG
# Unzip the data
unzip 'Data Files.zip'
# move files to desired path
mv 'Data Files'/* .
# OPTIONAL: remove unnecessary files
rm -r 'Data Files'Before proceeding with the processing stage of BCG dataset, the Matlab's script code/process/core/bcg_mat2csv.m must be run with the raw data path as parameter.
cd /bp_benchmark/code/process/core/bcg_mat2csv.m
matlab -r "bcg_mat2csv('../../../datasets/raw/BCG')"- PPGBP dataset might be found in Figshare's site.
mkdir /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/PPGBP
cd /bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/PPGBP
# Download PPGBP dataset under datasets/raw/PPGBP
wget -O data.zip https://figshare.com/ndownloader/files/9441097
# Unzip the data
unzip data.zip
# move files to desired path
mv 'Data File'/* .
# OPTIONAL: remove unnecessary files
rm -r 'Data File' data.zip This preprocessing pipeline allows the user to prepare the datasets to their use in the training pipeline later on. Starting from the original-raw datasets downloaded in bp_benchmark/datasets/raw/ , the pipeline performs the preprocessing steps of formating and segmentation, cleaning of distorted signals, feature extraction and data splitting for model validation.
process.py --config_file [CONFIG PATH]
- It performs the complete preparation of the datasets. (segmenting -> cleaning -> splitting)
- [CONFIG PATH]: provide the path of a config file, all config files can be found in
/bp_benchmark/code/process/core/config - Note: The preprocessing outcomes are two pickle files, for example, sensors.pkl (waveform data) & sensors_feats.pkl (feature data). These can be used to train the models if the training config files are changed accordingly. Alternatively, one can run share_dataset.py (in code/process) to export the files in mat and CSV format.
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/process
cd /bp_benchmark/code/process
python process.py --config_file core/config/sensors_process.yamlThe processed datasets are saved in the directories indicated in the config files of each processing steps at /bp_benchmark/code/process/core/config. By default, the datasets are saved under the directory /bp_benchmark/datasets in the following structure:
./raw: gathers the directories with the original data of each dataset (BCG, PPGBP, sensors & UCI)../segmented: stores the segmented datasets../preprocessed: keeps the cleaned datasets (signals and features)../splitted: stores the splitted data ready for training and validation.
Besides, the code has been modularized to be able to perform each of the data preparation steps independently. There are different three modules:
- Segmenting module: reads, aligns and segments the raw data according to the config file passed as
--config_fileparameter.- There are one script for each dataset with the name
read_<data-name>.py. - All config files of segmenting module are in
./core/config/segmentation
- There are one script for each dataset with the name
# In /bp_benchmark/code/process directory
python read_sensors.py --config_file core/config/segmentation/sensors_read.yaml- Preprocessing module: cleans the segmented signals and extracts the PPG's features.
cleaning.pyis the main script of the module. For PPG-BP dataset, please usecleaningPPGBP.py.- Its config files are located in
./core/config/preprocessing.
# In /bp_benchmark/code/process directory
python cleaning.py --config_file core/config/preprocessing/sensors_clean.yaml- Splitting module: splits the data according to the validation strategy chosen in the config file of
--config_fileparameter.data_splitting.pyis the main script of the module.- All config files are in
./core/config/splitting.
# In /bp_benchmark/code/process directory
python data_splitting.py --config_file core/config/preprocessing/sensors_clean.yamltrain.py --config_file [CONFIG PATH]
- It trains the model with the parameters set in the input config file.
- [CONFIG PATH]: provide the path of a config file, all config files can be found in
/bp_benchmark/code/train/core/config
- All the config files of Feat2Lab approach are in
./core/config/ml/
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python train.py --config_file core/config/ml/lgb/lgb_bcg_SP.yaml
- All the config files of Feat2Lab approach are in
./core/config/dl/resnet/
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python train.py --config_file core/config/dl/resnet/resnet_bcg.yaml
- All the config files of Feat2Lab approach are in
./core/config/dl/unet/
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python train.py --config_file core/config/dl/unet/unet_bcg.yaml
The models are save in the path indicated in the config_file (${path.model_directory}), by default it will be in /bp_benchmark/code/train/model-${exp.model_type}.
tune.py -m
- The input of tune.py is the config_file which is assigned in this script. People can edit the config path in the script.
- The parameter search space is defined in the config_file with Hydra optuna tool.
-mis the flag to do tune the parameters for multi run, without giving-m, it won't tune the parameters in search space, but only run with the paramters set in config_file (${param_model}) once.
- Edit the config file's path in
tune_ml.py
#============== In tune.py ==============#
# Edit the config file's path in following line:
@hydra.main(config_path='./core/config/tune/ml', config_name="lgb_sensors_SP")
#======= In command line interface ======#
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python tune_ml.py -m
- Edit the config file's path in
tune.py
#============== In tune.py ==============#
# Edit the config file's path in following line:
@hydra.main(config_path='./core/config/tune/dl', config_name="resnet_bcg_tune")
#======= In command line interface ======#
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python tune.py -m
test.py --config_file [CONFIG PATH]
- It tests on test set with the trained models specified in the input config file.
- [CONFIG PATH]: provide the path of a config file, all config files can be found in
/bp_benchmark/code/train/core/config/test
- All the config files of Feat2Lab approach are in
./core/config/test/dl/
# Go to /bp_benchmark/code/train
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
python test.py --config_file core/config/test/dl/ts_rsnt_bcg.yaml
Inference's example: code
# Setup mlflow server in background
# Step 1: open a new session with tmux for mlflow
tmux new -s mlflow
# Step 2: in the new session setup mlflow server
cd /bp_benchmark/code/train
mlflow ui -h 0.0.0.0 -p 9181 --backend-store-uri ./mlruns/
# leave the session with ^B+D
# Step 3: forward the port 9181
ssh -N -f -L localhost:9181:localhost:9181 username@working_server -p [port to working_server] -i [ssh key to working_server]
# Step 4: now you can browse mlflow server in your browser
# open a new tab in your browser and type http://localhost:9181/This guideline helps to relate the features used in the Feat2Lab models with the description in the paper.
- Note: If the same feature is extracted from the different derivatives of the PPG signal, they will have the format
{ppg|vpg|apg|ppg4}_<type_feature>_<number>.- For example:
- FFT:
ppg_fft_peaks_0,ppg_fft_peaks_heights_0, &ppg_fft_peaks_neighbor_avgs_0. (Frequency-based features) histogram_down&histogram_up: Histograms of diastolic and systolic phases, respectively. (Operational)max_0&min_0: Location of maximum and minimum of PPG, VPG, APG, or PPG4 average cycle.max_neighbor_mean_0: Average of the neighbors around the maximum value.
- FFT:
- For example:
Frequency-based features: Most dominant frequency (ppg_fft_peaks_0), its magnitude (ppg_fft_peaks_heights_0), and the average magnitude nearby it (ppg_fft_peaks_neighbor_avgs_0).
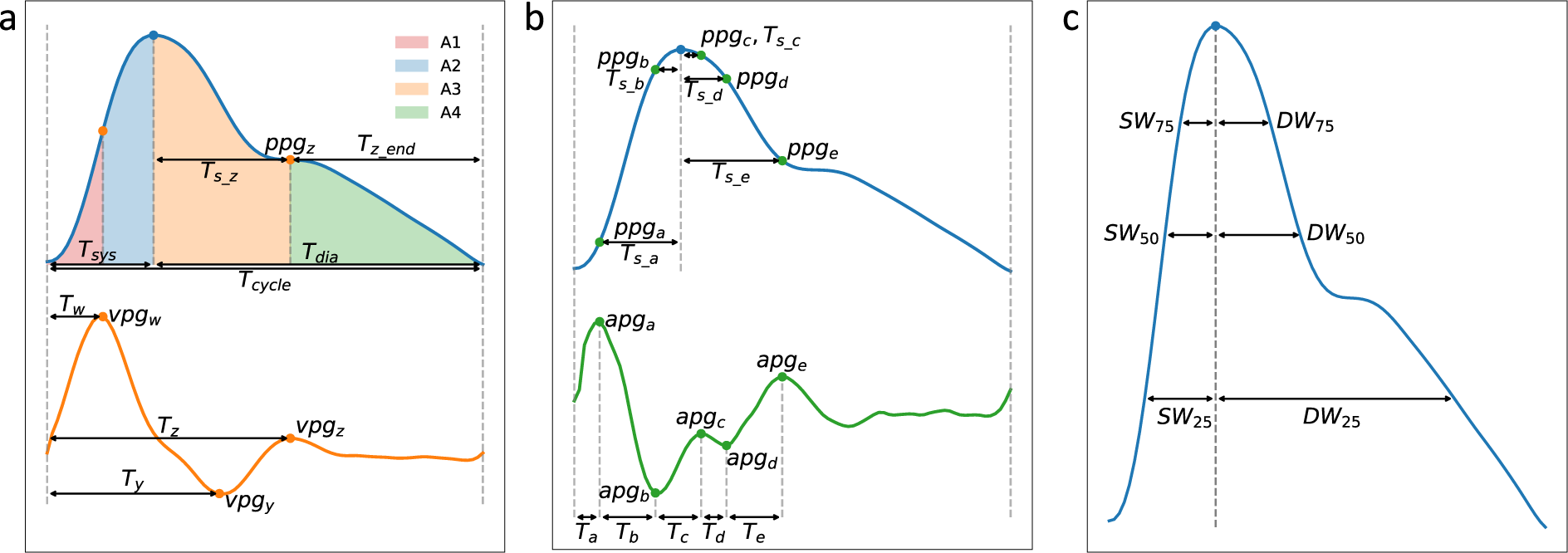
Points-of-interest and time-based features (paper's Fig. 9):
- (1) Amplitudes and (2) Elapsed times (Fig. 9a & 9b).
Tc,Ts,Td: Times of the cycle, systolic phase, and diastolic phase.Tsteepest,Steepest,TNegSteepest,NegSteepest,TdiaRise,DiaRise,SteepDiaRise,TSystoDiaRise,TdiaToEnd: Times and amplitudes of w (Steepest), y (NegSteepest) and z (DiaRise) points.apg_a,apg_b,apg_c,apg_d,apg_e,ppg_a,ppg_b,ppg_c,ppg_d,ppg_e: Amplitudes of those points (a,b,c,d,e) in APG and PPG.T_a,T_b,T_c,T_d,T_e,T_peak_a,T_peak_b,T_peak_c,T_peak_d,T_peak_e: Times for a,b,c,d,e explained in the paper.
- (3) Areas under the PPG curve (Fig. 9a):
S1,S2,S3,S4,AUCsys,AUCdia - (4) Widths (Fig. 9c):
SW,DW, their addition (SWaddDW), and ratio (DWdivSW).
Operational and statistical features:
- (1) Histogram features: Density values of the histogram for systolic phase (
histogram_up) and diastolic phase (histogram_down). - (2) Slope Deviation Curve (SDC) features:
usdc&dsdc(ref. paper [50]). - (3) SQI features:
SQI_skew,SQI_kurtosis. - (4) Indices features (ref. paper [51]):
AI,bd,bcda,sdoo.
This project is under the terms of the MIT license - Copyright (c) 2022 Inventec Corporation. Please reference this repository together with the relevant publication when using the code.
@article{BPbenchmark2023,
author = {Gonz{\'a}lez, Sergio and Hsieh, Wan-Ting and Chen, Trista Pei-Chun},
note = {(Inventec Corporation work)},
title = {A benchmark for machine-learning based non-invasive blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmogram},
journal = {Scientific Data},
volume={10},
number={1},
pages={149},
year={2023},
publisher={Nature Publishing Group UK London}
}