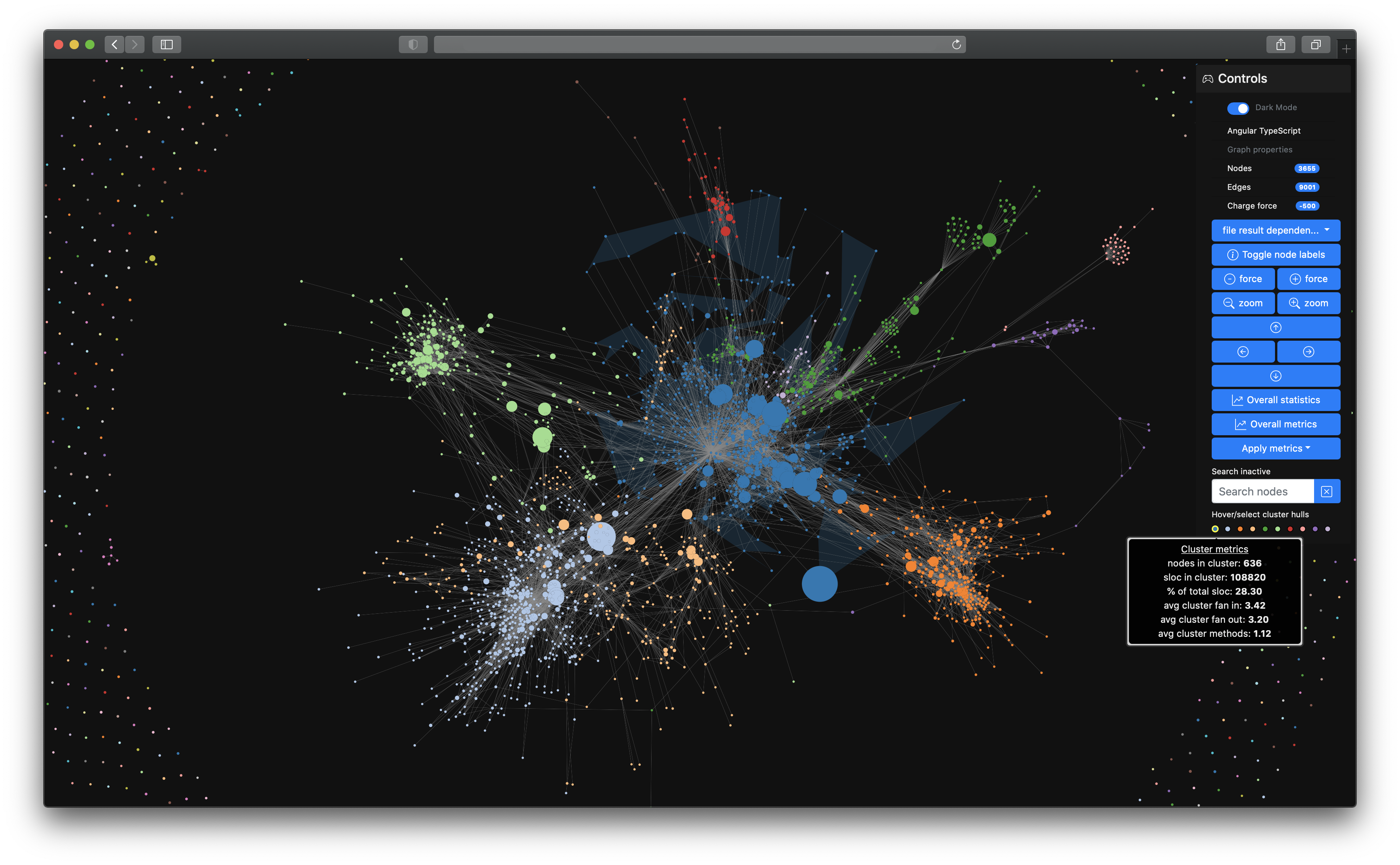
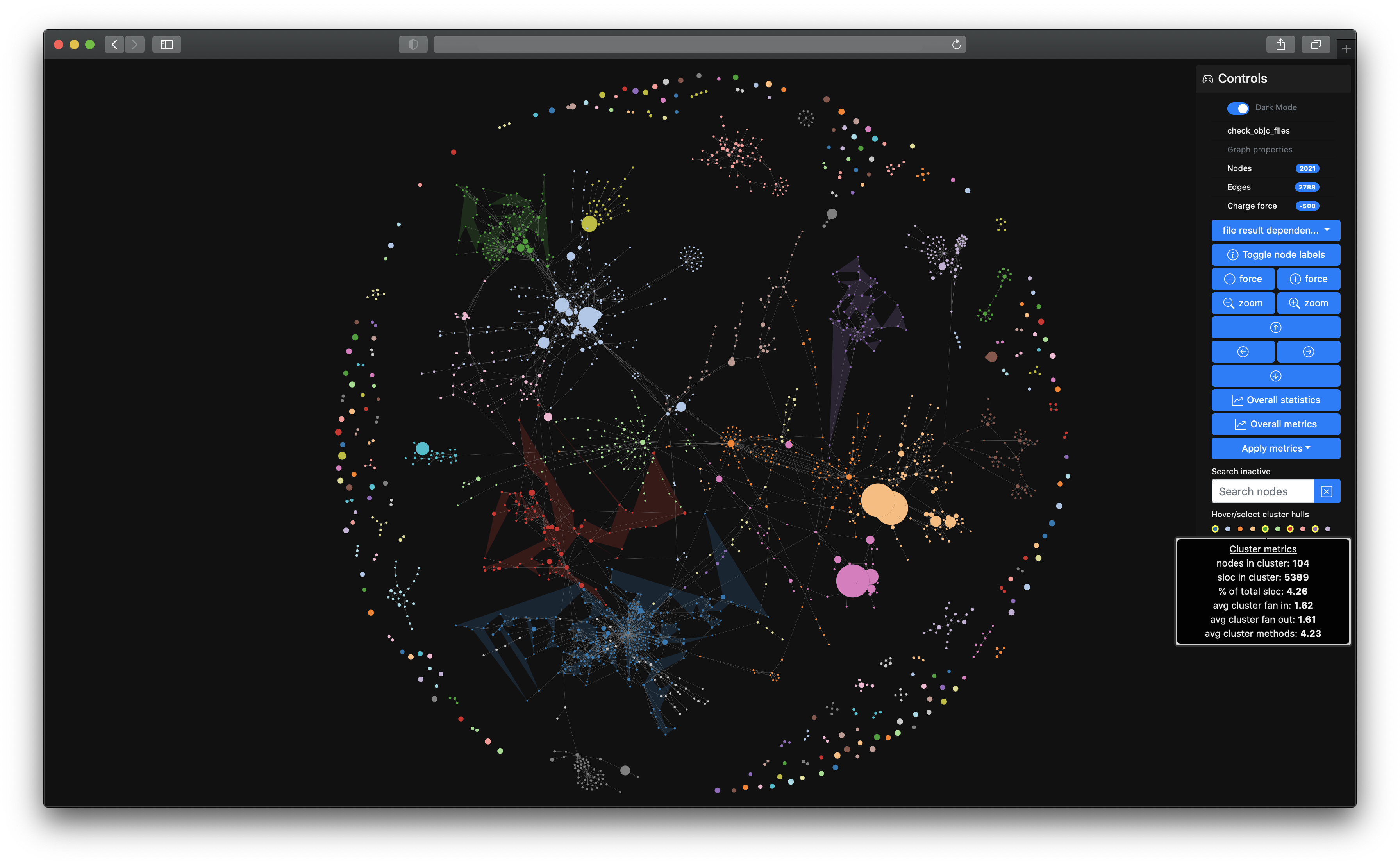
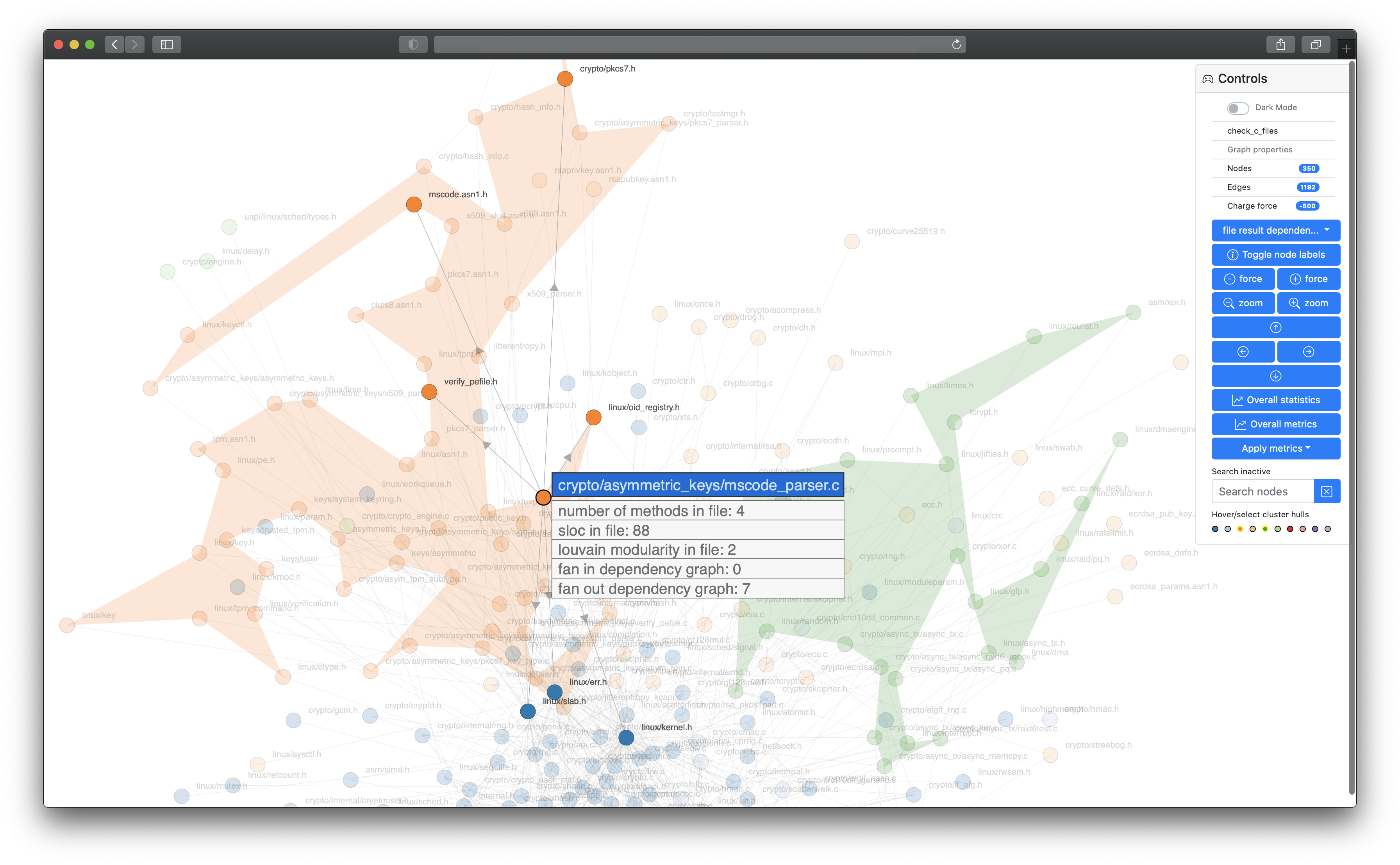
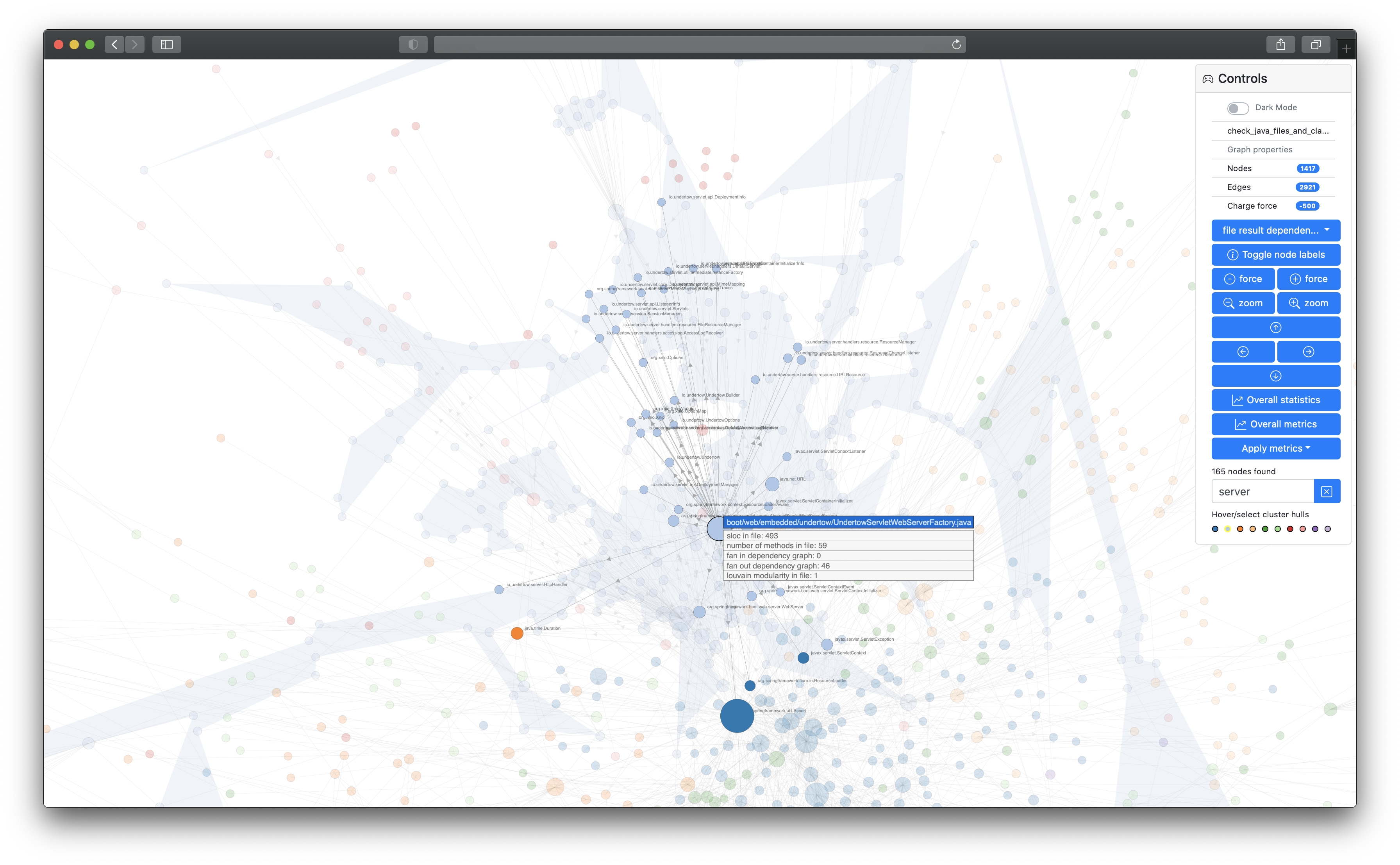
emerge is a code analysis tool to gather insights about source code structure, metrics, dependencies and complexity of software projects. You can use it to scan the source code of a project, calculate metric results and statistics, map the source code to graph structures (e.g. a dependency graph or a filesystem graph), export the results in other file formats and even create an interactive web application for further exploration. emerge currently has scanning support for the following languages: C, C++, Groovy, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Kotlin, ObjC, Ruby, Swift, Python. The structure, coloring and clustering is calculated and based on the idea of combining a force-directed graph simulation and Louvain modularity. emerge is mainly written in Python 3 and is tested on macOS, linux and modern web browsers (i.e. latest Safari, Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
emerge (/ɪˈməːdʒ/)
- to appear by coming out of something or out from behind something
- to become known, especially as a result of examining something or asking questions about it
The main goal of this project is to create a free/ open source tool, that can easily be used by anyone with interest in software development, architecture, metrics and visualization to gather more insights about those topics. It should facilitate/ support getting a better understanding of a given software project.
- File scan support for the following languages:
C,C++,Groovy,Java,JavaScript,TypeScript,Kotlin,ObjC,Ruby,Swift,Python - Basic entity scan/extraction (e.g. classes) for the following languages:
Groovy,Java,Kotlin,Swift - Basic implementation of the following software metrics: SLOC, Number of Methods, Fan-In/Fan-Out, Modularity (Louvain)
- Logging support with configurable log levels
- Configuration support based on YAML syntax to configure multiple/specific analyses
- Export of scan results/ metrics/ statistics for the following formats/ outputs
- Code dependency, inheritance, complete and filesystem graph (enriched with scan results/metrics)
- GraphML
- Graphviz DOT format
- JavaScript format suited for a D3 force graph simulation
- Interactive HTML/ web application for interactive, exploratory analysis and data visualization of your project based on graph structures
- HTML app is based on Bootstrap
- Force-directed graph simulation by D3
- The node colors are based on Louvain modularity with a bit of post-processing to make the graph coloring more deterministic and stable
- Fast full-screen UI rendering on HTML canvas
- Visualization of files, entities and given metrics
- dark mode support
- Reactive visual live search of files/ entities (e.g. classes)
- Concave hull visualization of single clusters
- Display of cluster metrics to facilitate comparability
- Interactivity given by translation, zooming, dragging and hovering over nodes
- Tabular console output
- Tabular file output
- JSON file output
At this time there is no simple installation by using pip (tbd), so the following steps should guide you how to install this tool and get it running.
1. Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/glato/emerge.git
2.1 (macOS) Install the graphviz package first
brew install graphviz
2.2 (macOS) Check of you have the latest Python 3 installed on your macOS. I recommend installing/using Python 3 from Homebrew. Create a Python 3 virtual environment (optionally within the project structure)
cd emerge
pip3 install virtualenv
virtualenv -p python3 venv
2. (ubuntu) Install required packages and create a Python 3 virtual environment (optionally within the project structure)
apt-get install python3-venv python3-dev graphviz graphviz-dev
cd emerge
python3 -m venv venv
3. Before using/working with the tool, activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
4. (macOS) Install all required dependencies for the project with pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
4. (ubuntu) Install the wheel package, after that install all required dependencies for the project with pip
pip install wheel
pip install -r requirements.txt
5. Running unit tests from the command line
python run_tests.py
6. Running EMERGE as a standalone tool
python emerge.py
usage: emerge.py [-h] [-c YAMLCONFIG] [-v] [-d] [-s]
Welcome to emerge x.y.z (yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss).
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c YAMLCONFIG, --config YAMLCONFIG
set yaml config file
-v, --verbose set logging level to INFO
-d, --debug set logging level to DEBUG
-s, --silent run silently without any console output
7. Create a YAML configuration for your scan or copy/adjust a template example from the configs directory. The template examples in emerge/configs should be mostly self-documenting. For a quick run, it's enough to adjust source_directory and directory in export.
---
project_name: c-example-project
loglevel: info
analyses:
- analysis_name: check_c_files
source_directory: /Users/user1/emerge/project/source/github/linux-5.8.5/crypto
only_permit_languages:
- c
only_permit_file_extensions:
- .c
- .h
ignore_dependencies_containing:
- string.h
file_scan:
- number_of_methods
- source_lines_of_code
- dependency_graph
- louvain_modularity
- fan_in_out
export:
- directory: /Users/user1/emerge/project/export
- graphml
- dot
- json
- tabular_file
- tabular_console_overall
- d38. Running EMERGE with a specific YAML configuration (e.g. a customized emerge/config/c-template.yaml)
python emerge.py -c configs/c-template.yaml
... which should produce a similar output:
... analysis I 👉 starting to analyze c-example-project
... analysis I ⏩ performing analysis 1/1: check_c_files
... analysis I 👉 starting token extraction for file results in check_c_files
... analysis I ⏩ starting scan at directory: .../github/linux-5.8.5/crypto
...
... analysis I ✅ scanning complete
... analysis I 👉 starting code metric calculation for analysis check_c_files
... analysis I ⏩ calculating metric results for: number of methods metric
... analysis I ⏩ calculating metric results for: source lines of code metric
... analysis I ✅ done calculating code metric results
... analysis I 👉 starting graph metric calculation for analysis check_c_files
... analysis I ⏩ calculating metric results for: louvain modularity metric
... analysis I ⏩ calculating metric results for: fan in out metric
... analysis I ✅ done calculating graph metric results
... emerge I ✅ successfully copied output to /Users/user1/emerge/project/export/force-graph-html
... analysis I 👉 the following statistics were collected in check_c_files
+-------------------------------------+-------------------+
| statistic name | value |
+-------------------------------------+-------------------+
| parsing_hits | 1196 |
| scanning_runtime | 00:00:06 + 424 ms |
| scanned_files | 163 |
| skipped_files | 16 |
| extracted_file_results | 163 |
| number-of-methods-metric-runtime | 00:00:40 + 331 ms |
| source-lines-of-code-metric-runtime | 00:00:00 + 99 ms |
| louvain-modularity-metric-runtime | 00:00:04 + 229 ms |
| fan-in-out-metric-runtime | 00:00:00 + 18 ms |
+-------------------------------------+-------------------+
... analysis I 👉 the following overall metrics were collected in check_c_files
+----------------------------------------------+------------------------------+
| metric name | value |
+----------------------------------------------+------------------------------+
| avg-number-of-methods-in-file | 17.91 |
| avg-sloc-in-file | 224.44 |
| louvain-communities-dependency-graph | 11 |
| louvain-modularity-dependency-graph | 0.44 |
| louvain-biggest-communities-dependency-graph | 0.24, 0.19, 0.14, 0.13, 0.11 |
| avg-fan-in-dependency-graph | 3.53 |
| avg-fan-out-dependency-graph | 3.53 |
| max-fan-in-dependency-graph | 132 |
| max-fan-in-name-dependency-graph | linux/module.h |
| max-fan-out-dependency-graph | 18 |
| max-fan-out-name-dependency-graph | testmgr.c |
+----------------------------------------------+------------------------------+
... analysis I ✅ all your generated/exported data can be found here: /Users/user1/emerge/project/export
... analysis I ✅ you can browse your interactive web app at: file:///Users/user1/emerge/project/export/force-graph-html/d3-force-graph-template.html
... analysis I ✅ calculated and collected metric data
... emerge I ✅ total runtime: 00:00:35 + 876 ms
After this your scan output (including your interactive web app) can be found at the directory that you created and set in the config parameter export -> directory, as seen in the logs above.
A full YAML configuration that contains both file and entity scan has the following format:
---
project_name: java_project_example
loglevel: info
analyses:
- analysis_name: check_java_files_and_classes
source_directory: /Users/user1/emerge/project/source
only_permit_languages:
- java
only_permit_file_extensions:
- .java
ignore_dependencies_containing:
- java.util
file_scan:
- number_of_methods
- source_lines_of_code
- dependency_graph
- fan_in_out
- louvain_modularity
entity_scan:
- dependency_graph
- source_lines_of_code
- number_of_methods
- fan_in_out
- louvain_modularity
export:
- directory: /Users/user1/emerge/project/export
- graphml
- dot
- json
- tabular_file
- tabular_console_overall
- d3The YAML configuration is basically defined at the following levels:
| key | value/ description |
|---|---|
project_name |
a project name for all analyses, scans and exports |
loglevel |
set a loglevel: error (silent, only errors), info (includes error) gives you basic logs about control flow, debug (includes info) will produce a lot of debug logs |
analyses |
an array of analyses that can be configured individually, thus a project can contain one to many analyses. |
| key | value/ description |
|---|---|
analysis_name |
a specific analysis name |
source_directory |
the source directory where the recursive file scan should start |
ignore_files_containing |
exclude file names from the scan that contain the given substrings |
ignore_directories_containing |
exclude directory names from the scan that contain the given substrings |
only_permit_languages |
possible values include: java, kotlin, objc, swift, ruby, groovy, javascript, c - explicitly prevents any other language from scanning besides the one you set here |
only_permit_file_extensions |
explicitly permit the following file extensions you set here, e.g. .java |
ignore_dependencies_containing |
ignore every dependency included in this list of substrings, e.g. java.util |
file_scan |
perform a file scan, contains the metrics that should be applied on every source file |
entity_scan |
perform an entity scan, contains the metrics that should be applied on every entity (e.g. on every class) |
export |
contains any export formats that should be create as output |
| key | value/ description |
|---|---|
dependency_graph |
create a dependency graph structure based on source files, additional metrics will be added to the graph nodes |
source_lines_of_code |
apply a source lines of code metric to every file, create an overall metric |
number_of_methods |
apply a number of methods metric to every file, create an overall metric |
fan_in_out |
apply a fan in/ fan out graph metric to every file, create an overall metric |
louvain_modularity |
apply a louvain modularity metric to every file, create an overall metric |
| key | value/ description |
|---|---|
dependency_graph |
create a dependency graph structure based on extracted entities from files, additional metrics will be added to the graph nodes |
inheritance_graph |
create an inheritance graph structure based on extracted entities from files, additional metrics will be added to the graph nodes |
complete_graph |
create a complete graph structure (union of dependency/ inheritance graph) based on extracted entities from files, additional metrics will be added to the graph nodes |
source_lines_of_code |
apply a source lines of code metric to every entity, create an overall metric |
number_of_methods |
apply a number of methods metric to every entity, create an overall metric |
fan_in_out |
apply a fan in/ fan out graph metric to every entity, create an overall metric |
louvain_modularity |
apply a louvain modularity metric to every entity, create an overall metric |
| key | value/ description |
|---|---|
directory |
the output directory for all specified export formats |
graphml |
create a graphML file that contains the graph structure and metric results mapped to the nodes of the graph |
tabular_file |
create a tabular formatted text file that contains every metric and statistic result |
tabular_console |
print a tabular formatted output to console that contains every metric and statistic result |
tabular_console_overall |
print a tabular formatted output to console that contains only overall metric and statistic results |
json |
create a JSON file that contains every metric and statistic result |
dot |
create a DOT file that contains the graph structure and metric results mapped to the nodes of the graph |
d3 |
create a Bootstrap/D3 web application in the subfolder force-graph-html for further visual and interactive/ exploratory analysis |
| Parsing | Groovy | Java | Kotlin | Swift | Ruby | JS | TS | ObjC | C/C++ | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Files | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Entities | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
- Parsing of further entity types for more languages is planned for further development. Contributions are welcome 👍
- Disclaimer: The current version (0.18.1) is not yet stable, probably still has some 🐞 and is probably not yet suited for productive usage.
- Everyone is invited to contribute to this project, whether the contribution is related with development, testing, bug reporting or any other support. I would appreciate any help 👍. See Contributing and Credits for further details.