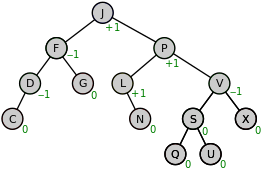
Rudimentary AVL Tree library implementation
To install use the following commands
go get github.com/rigelrozanski/AVL_Treego get golang.org/x/crypto/sha3
The AVL Tree is data storage structure which allows for the efficient retrieval of key-value pair data. It is an example of a self-balancing binary tree.The basic premise of a binary tree is that keys are linked to up to two childed keys where the left child has a key with a lesser value than its parents, and right child with a greater value.The AVL Tree by definition must always have a balance factor between (incl.) -1 and 1 where a balance factor is defined as the height of the right child node subtract the left child node. As such, an AVL Tree must reorganize itself through 'rotating' its nodes to achieve an appropriate balance factor. By maintaining a rough balance, and minimum overall height the number of operations required when searching for a record is minimized.
Further readings:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVL_tree
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/avl_tree_algorithm.htm
http://eniac.cs.qc.cuny.edu/andrew/csci700-11/lecture7.pdf
- This library implements rigorous use functions, and function variables to eliminate code duplication
- Core functionality is divided into node.go and tree.go
- node.go
- Defines the node struct and node type functions
- Node type methods are unexposed
- Generally handles micro management tasks of nodes including:
- Searching through sub nodes for matching keys or insert position
- Retrieving node balance
- Performing node rotation
- Performing rebalancing operations
- Removing records and performing rearrangement task post-removal
- Redefining the tree trunk when the uppermost node has changed
- Recursively updating balance, height, and merkle-hash values
- Recursively outputting elements
- tree.go
- Defines the tree struct and tree type functions
- Tree type methods are all exposed considered to be the main use functions of this library
- Generally handles macro tasks of the tree through piecing together node type functions
- node.go
- One key facet of this implementation of AVL Tree is that each node contains awareness of not only its children nodes but also its parent node. By a node storing the address of its parent nodes, all operations that may cause an affect on the height, balance, and hash values can be calculated at the area of action and recursively recalculated upwards (leaf-to-trunk) thus minimizing the total number operations in comparison to requiring to recalculate height/balance/hash values for the entire tree after every relevant operation. For further thoughts this see this link
- Another important implementation feature is the use of placeholder nodes in all the empty children of 'real' nodes. Placeholder nodes are not considered is height or balance operations, there are effectively not considered by any tree calculations. Placeholder nodes serve the purpose of providing orientation information for new nodes that will be added to the tree which allows the use of the same method for either searching for an existing node to retrieve or searching for a placement position for when adding a new node.
This basic implementation of an AVL Tree allows add, update, and remove values. Demonstration usage of the library can be seen within the testing files (notably tree_test.go). The exposed functions for the AVL Tree (listed within types.go) are as follows:
- GetHash() (hash []byte, err error)
- Returns the Merkle hash bytes for trunk node of the tree
- Generates an error if tree is empty
- Get(key []byte) (value []byte, err error)
- Returns the value bytes retrieved from a key
- Generates an error if the key doesn't exist
- Set(key, value []byte) error
- Performs an Add operation if key doesn't exist or an Update operation if it does
- Error return exists for consistency, it should not be generated provided that Add and Update are working as expected
- Add(key, value []byte) error
- Adds a new key-value pair to the tree
- Generates an error if the key is already in use within the tree
- Update(key, value []byte) error
- Updates the value in an existing key-value pair held within the tree
- Generates an error if the key is non-existent within the tree
- Remove(key []byte) error
- Removes a key-value pair from the tree based on key input
- Generates an error if the key is non-existent within the tree
- TreeStructure() string
- Returns a string which lists all the tree's node: keys, values, and position
The following code is a simple working usage example of the AVL_Tree package
package main
import (
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
avl "github.com/rigelrozanski/AVL_Tree"
)
func main() {
//The AVLTree to be tested with
tr := avl.NewAVLTree()
printErr := func(err error) {
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
}
//Add values using the Add function
fmt.Println("Adding some nodes with keys: a, b, c")
printErr(tr.Add([]byte("a"), []byte("valueA")))
printErr(tr.Add([]byte("b"), []byte("valueB")))
printErr(tr.Add([]byte("c"), []byte("valueC")))
fmt.Println("Current Tree Structure:")
fmt.Println(tr.TreeStructure())
//Add values using the Set function
fmt.Println("Adding some nodes with keys: d, e")
printErr(tr.Set([]byte("d"), []byte("valueD")))
printErr(tr.Set([]byte("e"), []byte("valueE")))
fmt.Println("Current Tree Structure:")
fmt.Println(tr.TreeStructure())
fmt.Println("Current Merkle Hash (in hex):")
hash1, err1 := tr.GetHash()
if err1 == nil {
fmt.Println(hex.EncodeToString(hash1[:]))
} else {
printErr(err1)
}
//Retrieve Saved values for a and d
retrieve := func(key string) {
val, err := tr.Get([]byte(key))
if err == nil {
fmt.Println("value stored under '" + key + "' is: " + string(val[:]))
} else {
printErr(err)
}
}
fmt.Println("\nAttempting to access values for keys 'a' and 'd'")
retrieve("a")
retrieve("d")
//Change values for a and d using the Update and Set commands
fmt.Println("\nChanging values for keys 'a' and 'd'")
printErr(tr.Update([]byte("a"), []byte("ChangedValueA")))
printErr(tr.Set([]byte("d"), []byte("ChangedValueD")))
retrieve("a")
retrieve("d")
//Removing values
fmt.Println("\nRemoving values for keys 'a'")
printErr(tr.Remove([]byte("a")))
fmt.Println("Current Tree Structure:")
fmt.Println(tr.TreeStructure())
fmt.Println("Removing values for keys 'd'")
printErr(tr.Remove([]byte("d")))
fmt.Println("Current Tree Structure:")
fmt.Println(tr.TreeStructure())
fmt.Println("Attempting to access values for keys 'a' and 'd'")
retrieve("a")
retrieve("d")
fmt.Println("\nCurrent Merkle Hash (in hex):")
hash2, err2 := tr.GetHash()
if err2 == nil {
fmt.Println(hex.EncodeToString(hash2[:]))
} else {
printErr(err2)
}
}
Code can be tested using the command from terminal once navigated to the AVL_Tree directory using
go test or alternatively with the the verbose flag using go test -v. If the verbose flag is used
testing output will include logged information describing the tree structure created during testing.
- Fork it
- Create your feature branch (git checkout -b my-new-feature)
- Commit your changes (git commit -am 'Add some feature')
- Push to the branch (git push origin my-new-feature)
- Create new Pull Request
AVL_Tree is released under the Apache 2.0 license.